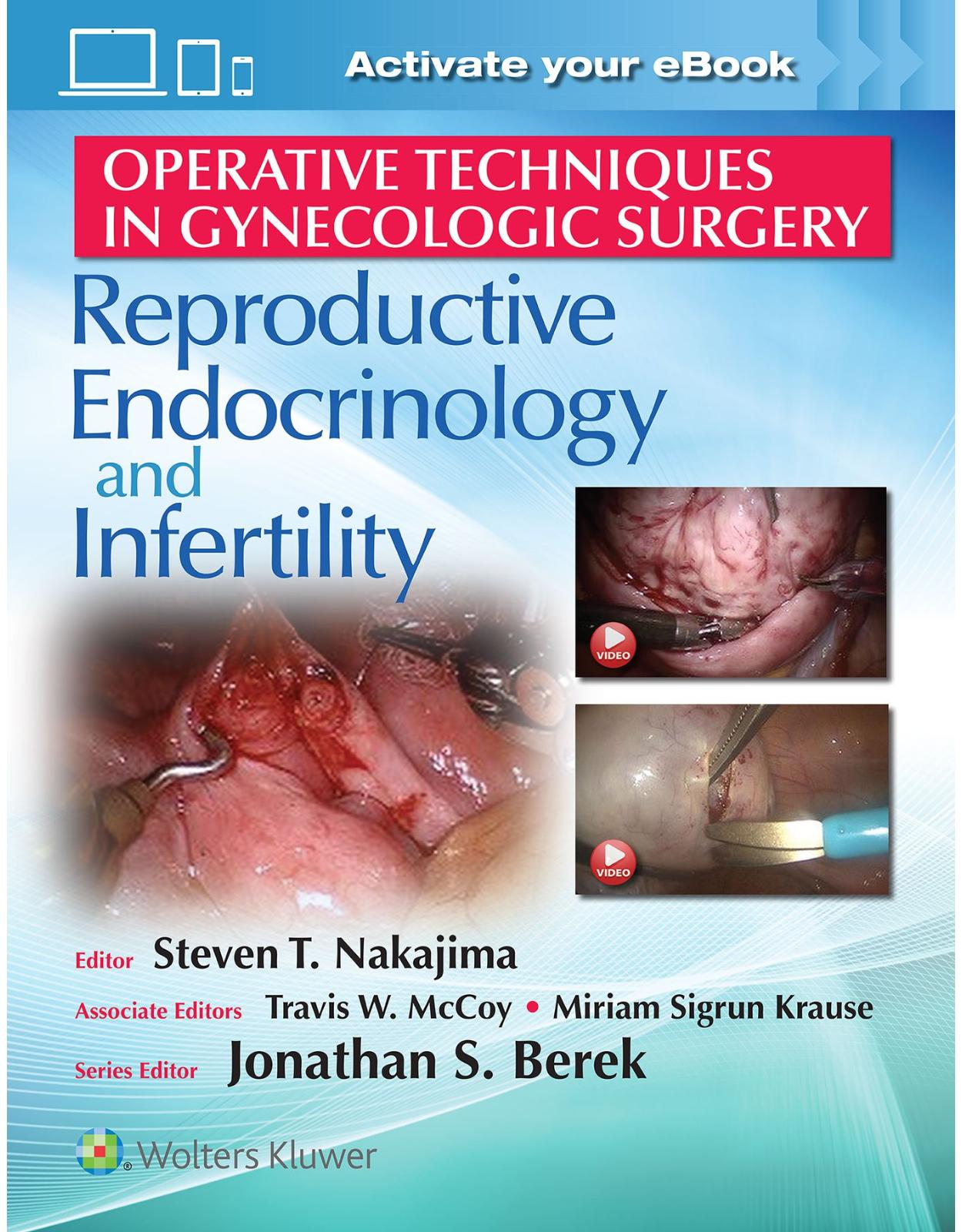
Minimally Invasive Therapies for Endocrine Neck Diseases
Livrare gratis la comenzi peste 500 RON. Pentru celelalte comenzi livrarea este 20 RON.
Disponibilitate: La comanda in aproximativ 4-6 saptamani
Editura: Springer
Limba: Engleza
Nr. pagini: 308
Coperta: Paperback
Dimensiuni: 155 x 235 x 25 mm
An aparitie: 14 Sep 2015
Description:
This handy book offers a complete overview of current minimally invasive techniques for the management of endocrine diseases of the neck, reflecting how, in the past few years, the development of various ultrasound-guided procedures and endoscopic/video-assisted surgical techniques has changed the approach to thyroid and parathyroid diseases. The book opens by describing the main diagnostic tools for thyroid, parathyroid and cervical lymph nodes, focusing especially on the new technologies for tissue characterization. The different minimally invasive treatment procedures involving either a percutaneous approach (ethanol injection, laser thermal ablation, radiofrequency thermal ablation, high-intensity focused ultrasound) or minimally invasive surgery are then described in detail. The volume is intended for all clinicians and surgeons with an interest in the field of endocrinology and neck surgery. It provides a synthetic but clear description of the various available techniques from a technical point of view and discusses the main issues concerning each of them, permitting comparative evaluation in order to identify the best option in a particular case. It also reports the evidence available in the current literature.
Table of Contents:
Part I: Ultrasound Imaging
1: Ultrasound Features of Thyroid, Parathyroid, Neck Lymph Nodes: Normal and Pathologic Pattern
1.1 Thyroid
1.1.1 Normal Neck Anatomy and Standard Ultrasound Examination
1.1.2 Diffuse Thyroid Enlargement
1.1.3 Focal Enlargement
1.1.3.1 Echogenicity
1.1.3.2 Calcifications
1.1.3.3 Margins
1.1.3.4 Halo
1.1.3.5 Vascularization
1.1.3.6 Taller Than Wide
1.1.3.7 Stiffness
1.1.3.8 Associated Features
1.2 Neck Lymph Node
1.3 Parathyroid
References
2: Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
2.1 Procedure
2.2 Contraindications
2.3 Complications
2.4 Thyroglobulin in Washout Fluid from Lymph Node FNAB
References
3: Cytology of Thyroid Lesions
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Non-neoplastic Lesions
3.3 Indeterminate Lesions
3.4 Suspicious for Malignancy
3.5 Malignant Neoplasms
3.6 Reporting Systems for Thyroid Cytology
References
4: Molecular Markers in Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsies
4.1 FNAB Material Retrieval, Conservation, Work-Up
4.2 Assessment of Molecular Abnormality in Cytological Sample
4.2.1 MicroRNA
4.2.2 Gene Mutations
4.2.3 Gene Translocations
4.2.4 Gene Amplifications
4.2.5 Gene Expression Variation
4.2.6 Aberrant Gene Methylation
4.2.7 Veracyte Afirma Gene Expression Classifier (GEC): Analytical and Clinical Value
4.3 Impact on Diagnosis
4.4 Impact on Surgical Choice
4.5 Future Perspectives
References
Part II: Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Techniques
5: Percutaneous Ethanol Injection for the Management of Thyroid Lesions
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Cytological Assessment
5.2.1 Technique
5.2.1.1 Cystic Nodules
5.2.1.2 Viscous Cystic Nodules
5.2.1.3 Complex Nodules
5.2.1.4 Solid Nodules
5.2.2 Assessment of the Response to PEIT
5.2.3 Side Effects
5.3 PEIT of Thyroid Cysts
5.3.1 Rationale
5.3.2 Results
5.3.3 Indications for Clinical Practice
5.4 Autonomously Functioning Thyroid Nodules (AFTNs)
5.4.1 Rationale
5.4.2 Results
5.4.3 Indications for Clinical Practice
5.5 Cold Nodules
5.5.1 Rationale
5.5.2 Results
5.5.3 Indications for Clinical Practice
5.6 Cervical Metastasis of Thyroid Cancer
5.6.1 Rationale
5.6.2 Results
5.6.3 Indications for Clinical Practice
5.7 Other Neck Lesions
5.8 Costs
Conclusions
References
6: Percutaneous Laser Thermal Ablation (LAT): Techniques, Indications, Experience and Complications
6.1 Principles and Technique
6.2 Experience
6.2.1 Cold Nodules
6.2.2 Autonomously Functioning Thyroid Nodules
6.2.3 Cystic Lesions
6.2.4 Cervical Recurrences of Thyroid Tumours
6.3 Tolerability and Safety
6.3.1 Tolerability
6.3.2 Complications
6.4 Conclusions and Indications
References
7: Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Procedure
7.2.1 Devices
7.2.2 The Trans-isthmic Approach and Moving Shot Technique
7.3 Indications
7.4 Clinical Outcomes
7.5 Complications
Conclusion
References
8: High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ablation (HI-FU) in Endocrine Neck Diseases
8.1 Technique
8.2 Indications
8.2.1 Thyroid Disease
8.2.1.1 Euthyroid Nodular Goiters
8.2.1.2 Nodular Hyperthyroidism
8.2.1.3 Not Estimated Indications
8.2.2 Parathyroid Neck Disease
8.3 Experience and Complications
8.4 Management of Complications
Conclusion
References
9: Mini-Invasive Techniques for the Treatment of Thyroid Nodules: Critical Issues
9.1 PEI
9.2 Laser and Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation
9.2.1 Are There US or Clinical Features or Physical Parameters Which Can Predict the Extent of Vo
9.2.2 What Is the Best Nodule Volume for Treatment?
9.2.3 Is Thermal Ablation Better Than PEI in Cystic Nodules? Is There a Limit in the Solid/Coll
9.2.4 How Frequent Is Nodule Regrowth? How Long Does Volume Reduction Last?
9.2.5 Is a Single Treatment Session Enough? How Many Repeated Treatment Sessions Are Required to
9.2.6 Are the Hyperfunctioning Nodules Suitable for Thermal Ablation?
9.2.7 Is There a Risk of Not Detecting Malignancy in Nodules Undergoing Thermal Ablation?
9.2.8 Is There a Precocious Thyroid Hormone Release After Treatment Causing Risk of Transient Thy
9.2.9 Is Thermal Ablation Cost-Effective?
9.2.10 Is Thermal Ablation Suitable for Treating Thyroid Cancer?
9.2.10.1 Local Recurrent Thyroid Cancer
9.2.10.2 Primary Tumor
9.2.11 Is a Technique (Laser or Radiofrequency) More Effective Than the Other?
9.3 HIFU
9.4 Microwave
References
Part III: Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
10: Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Thyroidectomy (MIVAT)
10.1 Introduction
10.2 Indications
10.3 Instruments
10.4 Surgical Technique
10.4.1 Anaesthesia
10.4.2 Patient Position
10.4.3 Surgical Equipment
10.4.4 Surgical Steps
10.5 Personal Series
10.6 MIVAT: Evidence-Based Recommendations
References
11: Locoregional Anesthesia in Thyroid and Parathyroid Surgery
11.1 Introduction
11.2 Benefits of Locoregional Anesthesia
11.3 Contraindications to Locoregional Anesthesia
11.4 Relevant Anatomy
11.5 Types of Locoregional Block
11.6 Types of Local Anesthesia
11.7 Monitored Anesthesia Care
11.8 Patient Selection
11.9 Complications Specific to Locoregional Anesthesia
Conclusion
References
12: Robotic Thyroidectomy
12.1 Remote Access Robotic Thyroidectomy Techniques
12.1.1 RAT Technique
12.1.2 RFT Technique
12.2 Indications for Remote Access Robotic Thyroid Surgery
12.2.1 RAT Patient Selection
12.2.2 RFT Patient Selection
12.3 Experience and Complications
12.3.1 RAT Outcomes
12.3.2 RFT Outcomes
12.4 Management of Complications
References
13: Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Parathyroidectomy (MIVAP)
13.1 Introduction
13.2 Surgical Technique
13.3 Indications
13.4 Experience and Complications
13.5 Advantages and Disadvantages
13.6 Avoiding Complications
13.6.1 Postoperative Hematoma
13.6.2 Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury
13.6.3 Hypocalcemia and Hypoparathyroidism
References
14: Endoscopic Parathyroidectomy
14.1 Techniques
14.1.1 Minimally Invasive Radioguided Approach (MIRP)
14.1.2 Open Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy (OMIP)
14.1.3 Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Parathyroidectomy (MIVAP)
14.1.4 Endoscopic Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy (EMIP)
14.1.5 Lateral Endoscopic Parathyroidectomy
14.1.6 Robotic Transaxillary Parathyroidectomy
14.2 Indications
14.3 Experience and Complications
14.4 Management of Complications
Conclusions
References
15: Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Neck Dissection
15.1 Introduction
15.1.1 Video-Assisted Central Compartment Dissection (VA-CCD)
15.1.2 Video-Assisted Lateral Neck Dissection (VALNED)
15.2 Indications
15.3 Surgical Technique
15.4 Personal Experience and Complications
References
16: Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques: Critical Appraisal and Future Perspectives
16.1 Parathyroidectomy
16.2 Thyroidectomy
References
Part IV: Intraoperative Adjuncts
17: Superior Laryngeal Nerve Monitoring
17.1 Introduction
17.2 EBSLN Surgical Anatomy
17.2.1 Classifications
17.2.2 The Sternothyroid–Laryngeal Triangle
17.2.3 EBSLN Anastomoses
17.3 Incidence of EBSLN Injury
17.4 Diagnosis and Treatment of the EBSLN Injury
17.5 EBSLN Monitoring Technique
17.5.1 Equipment and Setup
17.5.2 Definitions of EBSLN Monitoring
17.6 Technique A
17.6.1 IONM of the EBSLN: Stimulation–CTM Twitch [5]
17.7 Technique B
17.7.1 IONM of the EBSLN: Stimulation–Glottic EMG Signal [5]
17.7.2 Normative Data of the EBSLN Monitoring
Conclusion
References
18: Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Monitoring
18.1 Applications of IONM
18.2 Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring Standards
18.2.1 Introduction
18.2.2 Technique: IONM
18.2.3 The Equipment Setup
18.2.4 Anesthesia
18.2.5 Loss of Signal and Its Interpretation (Fig. 18.3)
18.2.6 Prognostic Testing Errors
18.3 Promising Advances in IONM
18.3.1 Continuous Vagal Monitoring and Neural Injury Prevention
18.3.2 Superior Laryngeal Nerve (SLN) Monitoring
18.3.3 Neural Monitoring and Staged Thyroidectomy in Thyroid Cancer Surgery: An Emerging Concept
18.3.4 Intraoperative Identification of Nonrecurrent Laryngeal Nerve
References
19: Hemostatic Devices
19.1 Introduction
19.2 Harmonic Scalpel
19.3 LigaSure
19.4 BiClamp
19.5 Comparison Between Devices
References
20: Topical Hemostatic Agents
20.1 Introduction
20.2 Indications
20.3 Topical Hemostatic Agents
20.3.1 Passive Hemostatics
20.3.1.1 Cellulose-Based Hemostatic Agents
20.3.1.2 Gelatin-Based Hemostatic Agents
20.3.1.3 Collagen-Based Hemostatic Agents
20.3.2 Active Hemostatics
20.3.2.1 Fibrin Sealants (FS)
20.3.2.2 Thrombin-Based Hemostatic Agents
20.3.3 Tissue Adhesive
20.3.4 Combined THA
20.4 Adverse Effects and Complications
20.4.1 Impaired Wound Healing
20.4.2 Surgical Infection
20.4.3 Allergic Reactions
20.4.4 Blood-Borne Disease
20.4.5 Vascular Thrombosis
20.5 Choice of Topical Hemostatic Agent
20.6 Cost Considerations
Conclusions
References
21: Critical Appraisal
21.1 Introduction
21.2 External Branch Superior Laryngeal Nerve Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring
21.3 Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring
21.4 Hemostatic Devices
21.5 Hemostatic Agents
Conclusion
References
Part V: Key-Points
22: How to Avoid and Manage Post-operative Complications
22.1 Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve/Voice Injury
22.1.1 Pre-operative Considerations
22.1.2 Operation
22.1.3 Post-operative Management
22.2 Haemorrhage/Haematoma
22.2.1 Pre-operative Considerations
22.2.2 Operation
22.2.3 Post-operative Management
22.3 Hypoparathyroidism
22.3.1 Pre-operative Considerations
22.3.2 Operation
22.3.3 Post-operative Management
22.4 Pain
22.5 Wound Complications
22.6 Rare Complications
22.7 Complaints and Litigation
References
23: Perioperative Medical Treatment
23.1 Preoperative Medical Management
23.2 Medical Treatment of Postsurgical Hypothyroidism
23.3 Medical Treatment of Postsurgical Hypoparathyroidism
References
24: Patient Counselling and Patients’ Involvement in Health Policy
24.1 For Physicians
24.1.1 Informed Patients
24.2 Informed Consent
24.2.1 New Technology and Innovative Surgical Treatments
24.2.2 Patients Organizations and Patients Advocates Role in Health Care Decision-Making Process
24.3 For Patients
24.3.1 Some Hints for Patients to Retrieve Correct Information from the Internet
24.3.2 How Can I Check the Quality of the Information I Find on the Web?
24.3.3 How Can I Choose my Surgeon?
24.3.4 Alternative Options for Benign Nodule Treatment
24.3.5 Thyroid Surgery
| An aparitie | 14 Sep 2015 |
| Autor | Celestino Pio Lombardi, Rocco Bellantone |
| Dimensiuni | 155 x 235 x 25 mm |
| Editura | Springer |
| Format | Paperback |
| ISBN | 9783319200644 |
| Limba | Engleza |
| Nr pag | 308 |