- 19%
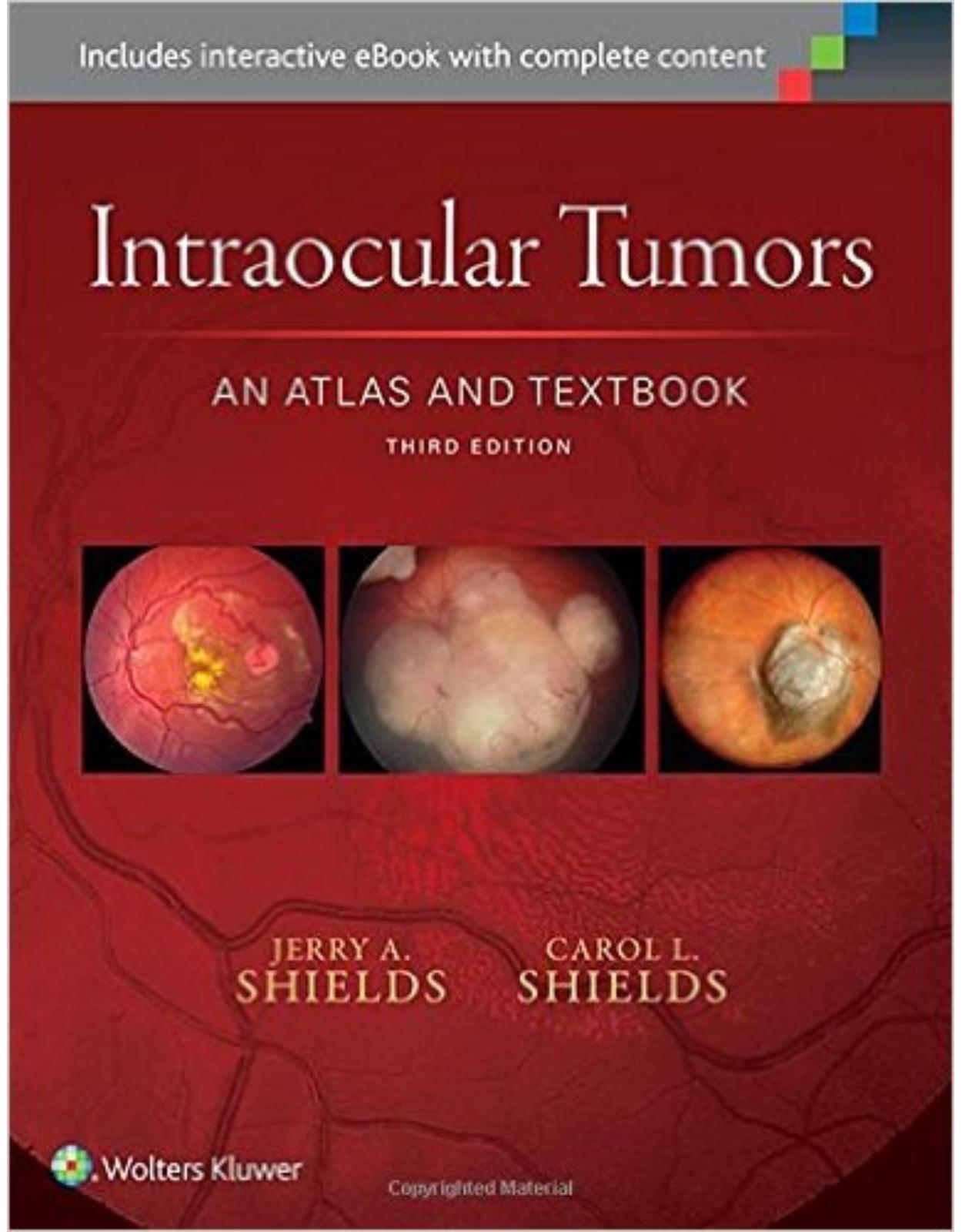
Intraocular Tumors: An Atlas and Textbook Third Edition
2087 Lei 1691 Lei(TVA inclus)
Livrare gratis la comenzi peste 500 RON. Pentru celelalte comenzi livrarea este 20 RON.
Livrare gratis la comenzi peste 500 RON. Pentru celelalte comenzi livrarea este 20 RON.
Cod produs/ISBN: 9781496321343
Disponibilitate: La comanda in aproximativ 4-6 saptamani
Editura: LWW
Limba: Engleza
Nr. pagini: 608
Coperta: Hardback
Dimensiuni: 21.8 x 2.3 x 28.2 cm
An aparitie: 2015
Description:
For outstanding visual clarity in ocular diagnosis … nothing else comes close.In this updated and revised third edition, world-renowned authorities at the Wills Eye Hospital provide outstanding guidance on recognition, evaluation, and treatment of ocular tumors, highlighted by more than 2,500 stunning photographs and surgical drawings. This unsurpassed ocular oncology resource is a comprehensive guide to the clinical features, diagnosis, management, and pathology of intraocular tumors and pseudotumors, depicting clinical variations, treatment, and histopathologic characteristics of the many varied benign and malignant lesions that affect the uveal tract, retina, and other intraocular structures. Now brought thoroughly up to date with recent clinical and scientific innovations, this unique volume has been greatly expanded with over 25% new material, and offers more high-quality images than any other text/atlas in the field
.•Presents each entity in an easy-to-follow format: a concise description with references on the left-hand page and six illustrations on the right-hand page.
•Depicts in precise photographic detail the gross and microscopic features that distinguish each condition, while professional drawings and intraoperative photographs demonstrate key surgical principles and procedures.
•Features numerous new references regarding diagnosis and treatment, as well as new scientific tables containing key information for your clinical practice.
•Features 25% new images, including panoramic images, surgical images, diagnostic testing images from multiple modalities, and updated OCT images with numerous enhanced depth imaging OCT (EDI-OCT)
.•Covers new information on evolving conditions such as the management of choroidal nevus and melanoma with guidance for early detection using risk factors; information on the newest treatment for retinoblastoma with intra-arterial and intravenous chemotherapy; management of intraocular tumors with photodynamic therapy. Important new information on genetics of uveal melanoma, the implications of genetics, and treatment outcomes is describedNow with the print edition, enjoy the bundled interactive digital edition, which can be downloaded to your tablet and smartphone or accessed online and includes features like:
•Complete content with enhanced navigation
•Powerful search tools and smart navigation cross-links that pull results from content in the book, your notes, and even the web
•Cross-linked pages, references, and more for easy navigation
•Highlighting tool for easier reference of key content throughout the text
•Ability to take and share notes with friends and colleagues
•Quick reference tabbing to save your favorite content for future use
Table of Contents:
Part 1: Tumors of the Uveal Tract
Chapter 1: Congenital Uveal Lesions
Intraocular Lacrimal Gland Choristoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Intraocular Lacrimal Gland Choristoma
Congenital Ocular Melanocytosis
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Congenital Ocular Melanocytosis: External Features
Congenital Ocular Melanocytosis: Fundus Features
Congenital Oculodermal Melanocytosis (Nevus of OTA) in Non-Caucasians
Uveal Melanoma Associated with Ocular and Oculodermal Melanocytosis
Multifocal and Bilateral Uveal Melanoma Associated with Congenital Ocular Melanocytosis
Diffuse and Sector Oculodermal Melanocytosis with Related Melanoma
Intracranial Melanoma Associated with Congenital Ocular Melanocytosis
Chapter 2: Melanocytic Tumors of Iris Stroma
Chapter 2 Introduction
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Imaging
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Table 2.1: The ABCDEF guide for factors predictive of iris nevus transformation into iris melanoma
Iris Freckle and Iris Nevus: Pigmented Variations
Iris Nevus: Nonpigmented and Minimally Pigmented Variations
Iris Nevus: Effects on Adjacent Structures
Iris Melanocytoma
Iris Melanocytoma with Secondary Glaucoma (Melanocytomalytic Glaucoma)
Iris Melanocytoma with Documented Growth
Iris Melanoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Table 2.2: Iris Melanoma based on American Joint Cancer Committee (AJCC, 7th edition) classification
Table 2.3: Cumulative metastasis and death from iris melanoma: Comparison between children, mid-adults, and older adults
Iris Melanoma: Pigmented Variations
Iris Melanoma: Nonpigmented Variations
Iris Melanoma: Atypical Clinical Variations
Iris Melanoma: Tapioca Type
Iris Melanoma: Tapioca Type Simulating Cogan–Reese Syndrome
Diffuse Iris Melanoma
Iris Melanoma Imaging with Ultrasound Biomicroscopy and Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography
Diffuse Iris Melanoma Managed with Enucleation
Diffuse Iris Melanoma Management
Diffuse Iris Melanoma Managed with Plaque Brachytherapy
Iris Melanoma in a Patient with Familial Atypical Mole Syndrome (Dysplastic Nevus Syndrome)
Iris Melanoma: Management by Sector Iridectomy and Iridogoniocyclectomy
Iris Melanoma: Management by Sector Iridectomy and Pupilloplasty
Iris Melanoma: Management of Unresectable Tumor by Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy and Plaque Radiotherapy
Iris Melanoma: Management of Unresectable Tumor with Plaque Radiotherapy
Chapter 3: Conditions That Simulate Iris Melanoma
Conditions That Simulate Iris Melanoma
Selected References
Table 3.1: Nonneoplastic lesions simulating iris tumor or melanoma
Iridocorneal Endothelial Syndrome
Iris Foreign Bodies That Simulate Iris Melanoma
Miscellaneous Nonneoplastic Conditions That Simulate Iris Melanoma
Miscellaneous Tumors That Simulate Iris Melanoma
Iris Pigment Epithelial Midzonal Cysts That Simulate Iris Melanoma
Chapter 4: Iris Cysts
Iris Cysts
Cysts of the Iris Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Table 4.1: Classification of iris cysts
Table 4.2: IPE cysts in 672 cases based on age at presentation
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Pupillary (Central) Type
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Pupillary (Central) Type Associated with Aortic Dissection
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Midzonal Type
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Midzonal Type with Massive Enlargement Requiring Needle Aspiration for Deflation
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Midzonal (Retroiridic) Type
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Free-Floating Type
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst: Free-Floating Type with Subsequent Fixation in Anterior Chamber Angle
Iris Stromal Cysts
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Table 4.3: Iris stromal cysts in 84 cases based on age at presentation
Iris Stromal Cyst: Congenital Type
Iris Stromal Cyst. Congenital Type: Management Was by Aspiration and Alcohol Irrigation
Iris Stromal Cyst: Primary Acquired Type
Iris Stromal Cyst: Imaging with Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography and Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Iris Stromal Cyst: Primary Acquired Type. Natural Course and Treatment
Iris Stromal Cyst: Secondary Acquired Type Following Nonsurgical and Surgical Trauma
Chapter 5: Choroidal Nevus
Chapter 5 Introduction
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Table 5.1: Choroidal nevus growth into melanoma based on risk factors in 2,514 consecutive cases. The mnemonic “To Find Small Ocular Melanoma Using Helpful Hints Daily”
Choroidal Nevus Pigmented Variations
Choroidal Nevus: Nonpigmented Variations
Choroidal Nevus: Clinical Variations
Choroidal Nevus: Effects on Adjacent Structures
Choroidal Nevus: Fluorescein Angiography
Choroidal Nevus: Optical Coherence Tomography
Choroidal Nevus: Autofluorescence
Choroidal Nevus: Growth into Choroidal Melanoma
Chapter 6: Melanocytoma of the Optic Disc and Posterior Uvea
Melanocytoma of the Optic Disc and Posterior Uvea
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Table 6.1: Outcomes of optic nerve melanocytoma
Optic Disc Melanocytoma
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Involvement
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Juxtapapillary Choroidal Involvement
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Fluorescein Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Associations and Clinical Variations
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Visual Loss from Tumor Necrosis
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Visual Loss from Central Retinal Vascular Obstruction
Optic Disc Melanocytoma: Evolution into Malignant Melanoma
Ciliary Body Melanocytoma
Choroidal Melanocytoma
Choroidal Melanocytoma: Giant Diffuse Variant Giving Rise to Melanoma in a Patient with Oculodermal Melanocytosis
Chapter 7: Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Clinical Features
Clinical Features of Posterior Uveal Melanoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features of Ciliary Body Melanoma
Clinical Features of Choroidal Melanoma
Spontaneous Regression of Choroidal Melanoma
Risk Factors for Growth and Metastasis of Small Melanocytic Choroidal Lesions
Classification of Posterior Uveal Melanoma Using the American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) Classification
Selected References
Table 7.1: Clinical features of posterior uveal melanoma in 7,748 eyes
Table 7.2: Factors for detection of small choroidal melanoma at tumor thickness ≤3 mm using the mnemonic “To Find Small Ocular Melanoma—Using Helpful Hints Daily”
Table 7.3: Prognosis of posterior uveal melanoma based on tumor thickness in 7,354 cases
Table 7.4: Classification of choroidal melanoma using the American Joint Commission on Cancer Classification (AJCC), 7th edition. Tumor category
Table 7.5: Posterior uveal melanoma category based on American Joint Cancer Committee (AJCC, 7th edition) classification subsets
Table 7.6: Staging of posterior uveal melanoma based on AJCC classification
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Sentinel Blood Vessels
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Transcleral Extension
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Iris Extension
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Appearance through a Dilated Pupil
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Wide-Angle Imaging
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Cavitary Variant
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Ring Variant with Extraocular Extension and Secondary Glaucoma
Choroidal Melanoma: Detection of Small Melanoma with Fundus Autofluorescence and Optical Coherence Tomography
Choroidal Melanoma: Pigmented Variations
Choroidal Melanoma: Partly Pigmented Variations
Choroidal Melanoma: Nonpigmented Variant
Choroidal Melanoma: Mushroom-Shaped Tumors with Pigmented Dome
Choroidal Melanoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Mushroom-Shaped Tumors with Pigmented Dome
Choroidal Melanoma: Mushroom-Shaped Tumors with Nonpigmented Dome
Choroidal Melanoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Mushroom-Shaped Tumors with Nonpigmented Dome. More Variations in Size and Shape of Choroidal Melanomas Are Shown
Choroidal Melanoma: Effects on Adjacent Structures
Choroidal Melanoma: Retinal and Vitreal Invasion
Choroidal Melanoma: Retinal Vein Dilation Secondary to Retinal Invasion
Choroidal Melanoma: Diffuse Growth Pattern
Choroidal Melanoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Diffuse Tumors
Choroidal Melanoma: Diffuse Tumor with Optic Nerve Invasion
Choroidal Melanoma: Diffuse Tumor Presenting as Atypical Extraocular Extension
Choroidal Melanoma: Advanced Tumor Presenting with Acute Glaucoma
Choroidal Melanoma: Advanced Tumor Presenting with Massive Extraocular Extension
Choroidal Melanoma: Intracranial Extension of Unsuspected Tumor Causing Bilateral Visual Loss
Choroidal Melanoma in Young Patients
Choroidal Melanoma in Non-Whites
Choroidal Melanoma: Spontaneous Necrosis and Regression
Chapter 8: Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Pathology
Pathology of Posterior Uveal Melanoma
Selected References
Table 8.1: Histopathologic features of uveal melanoma in 1,526 cases
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Gross Features
Choroidal Melanoma: Gross Features
Choroidal Melanoma: Mushroom-Shaped Configuration
Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Cell Types
Choroidal Melanoma: Clinicopathologic Correlations
Chapter 9: Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Diagnostic Approaches
Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Diagnostic Approaches
General Considerations
Transillumination
Fluorescein Angiography and Indocyanine Green Angiography
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Radioactive Phosphorus Uptake Test
Optical Coherence Tomography
Autofluorescence
Selected References
Choroidal Melanoma: Fluorescein Angiography of a Dome-Shaped Tumor
Choroidal Melanoma: Fluorescein Angiography of a Mushroom-Shaped Tumor
Choroidal Melanoma: Fluorescein Angiography of a Tumor with Overlying Choroidal Neovascular Membrane
Choroidal Melanoma: Indocyanine Green Angiography
Choroidal and Ciliary Body Melanoma: Ultrasonography And Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Choroidal and Ciliary Body Melanoma: Computed Tomography And Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Choroidal Melanoma: Enhanced Depth Imaging Optical Coherence Tomography
Choroidal Melanoma: Fundus Autofluorescence Imaging
Choroidal and Ciliary Body Melanoma: Radioactive Phosphorus Uptake Test And Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Choroidal Melanoma: Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Choroidal Melanoma: Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy in an Eye Presenting with Vitreous Hemorrhage
Choroidal Melanoma: Genetic Testing Using Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Chapter 10: Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Management
Chapter 10: Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Management
Observation
Laser Photocoagulation
Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Charged Particle Irradiation
Plaque Brachytherapy
Other Radiation Methods
Local Resection
Enucleation
Orbital Exenteration
Combination Methods
Genetic Studies
Systemic Treatment
Selected References
Choroidal Melanoma: Observation
Choroidal Melanoma: Small Tumors That Were Initially Observed and Eventually Showed Growth And Developed Metastasis
Choroidal Melanoma: Argon Laser Photocoagulation or Transpupillary Thermotherapy for Small Tumors
Choroidal Melanoma: Transpupillary Thermotherapy for Small Tumors
Choroidal Melanoma: Transpupillary Thermotherapy for a Small Tumor with Documented Growth
Choroidal Melanoma: Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Choroidal Melanoma: Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Choroidal Melanoma: Side Effects of Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Choroidal Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for Small- to Medium-Sized Tumors
Choroidal Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for Medium-Sized Tumors. Wide-Angle Imaging
Choroidal Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for Medium-Sized and Large Tumors. Wide-Angle Imaging
Choroidal Melanoma: Early Response to Plaque Radiotherapy
Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for Large Tumors
Choroidal Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for Mushroom-Shaped Tumors
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy
Choroidal Melanoma: Management of Juxtapapillary Melanoma with Plaque Radiotherapy and Thermotherapy
Choroidal Melanoma: Combined Plaque Radiotherapy and Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Ciliary Body Melanoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for a Tumor with an Extraocular Extension
Choroidal Melanoma: Ultrasonography Following Plaque Radiotherapy
Choroidal Melanoma: Side Effects of Plaque Radiotherapy
Ciliochoroidal Melanoma: Local Resection by Partial Lamellar Cyclochoroidectomy
Ciliochoroidal Melanoma: Local Resection by Partial Lamellar Cyclochoroidectomy in an Eye with Extensive Retinal Detachment
Ciliochoroidal Melanoma: Results of Partial Lamellar Sclerouvectomy. Long-Term Results
Choroidal Melanoma: Local Resection by Partial Lamellar Sclerochoroidectomy with 20-Year Follow-Up
Choroidal Melanoma: Enucleation for a Large Tumor. Wide-Angle Imaging by Equator-Plus Camera
Choroidal Melanoma: Enucleation for Large Tumors. Wide-Angle Imaging
Choroidal Melanoma: Enucleation for Small- and Medium-Sized Melanomas
Choroidal Melanoma: Enucleation for Small- and Medium-Sized Tumors
Choroidal Melanoma: Modified Enucleation Using a Lateral Orbitotomy Approach for a Tumor with Sizeable Orbital Extension
Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Orbital Exenteration and Modified Enucleation for Recurrent Orbital Tumor Following Treatment of Uveal Melanoma
Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Orbital Exenteration for a Tumor with a Massive Orbital Extension
Posterior Uveal Melanoma: Orbital Exenteration Following Evisceration Elsewhere for Unsuspected Uveal Melanoma That Simulated Endophthalmitis
Chapter 11: Nonneoplastic Conditions That Can Simulate Posterior Uveal Melanoma and Other Intraocular Neoplasms
Nonneoplastic Conditions That Can Simulate Posterior Uveal Melanoma and Other Intraocular Neoplasms
Selected References
Table 11.1: Choroidal pseudomelanomas in 1,739 cases. Top 30 diagnoses
Age-Related Macular Degeneration Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Peripheral Exudative Hemorrhagic Chorioretinopathy Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Peripheral Exudative Hemorrhagic Chorioretinopathy Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Retinal Arterial Macroaneurysm with Hemorrhage Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Miscellaneous Subretinal and Intraretinal Hemorrhages Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Choroidal Neovascular Membrane in Young Patients Simulating Choroidal Melanoma and Nevus
Choroidal Hemorrhage Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Vortex Vein Varix Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Nodular Posterior Scleritis Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Uveal Effusion Simulating Ciliochoroidal Melanoma
Choroidal Granulomas (Sarcoidosis and Tuberculosis) Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Solitary Idiopathic Choroiditis Simulating Amelanotic Choroidal Melanoma
Solitary Infectious Fundus Lesions Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Bilateral Diffuse Uveal Melanocytic Proliferation: Clinical Variations
Bilateral Diffuse Uveal Melanocytic Proliferation Simulating Uveal Melanoma
Miscellaneous Conditions Simulating Posterior Uveal Melanoma
Miscellaneous Other Conditions That Simulate Posterior Uveal Melanoma
Chapter 12: Metastatic Tumors to the Uvea, Retina, and Optic Disc
Metastatic Tumors to the Intraocular Structures
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Iris Metastasis from Breast Cancer
Iris Metastasis from Cutaneous Melanoma
Iris Metastasis from Miscellaneous Sites
Iridociliary and Ciliary Body Metastasis
Choroidal Metastasis from Breast Cancer
Choroidal Metastasis from Breast Cancer: Multifocal and Bilateral Tumors
Choroidal Metastasis from Lung Cancer
Choroidal Metastasis from Cutaneous Melanoma
Choroidal Metastasis from Choroidal Melanoma
Choroidal Metastasis from Carcinoid Tumors
Choroidal Metastasis from Kidney, Bile Duct, and Esophageal Carcinomas
Choroidal Metastasis from Undetermined Primary Sites, Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Uveal Metastasis from Sarcomas
Choroidal Metastasis: Effects on Adjacent Structures
Orange-Colored Choroidal Metastasis
Choroidal Metastasis: Pathology
Choroidal Metastasis: Metastasis from Lung Carcinoma Simulating Sarcoidosis
Mushroom-Shaped Choroidal Metastasis
Choroidal Metastasis: Clinicopathologic Correlation of Metastasis from an Undetermined Primary Neoplasm
Choroidal Metastasis: Fluorescein Angiography
Choroidal Metastasis: Ultrasonography
Choroidal Metastasis: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Choroidal Metastasis: Fundus Autofluorescence and Optical Coherence Tomography
Choroidal Metastasis: Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Choroidal Metastasis: Response to External Beam Radiotherapy
Choroidal Metastasis: Response to Plaque Radiotherapy
Choroidal Metastasis: Response to Photodynamic Therapy
Optic Disc Metastasis
Retinal and Vitreal Metastasis
Retinal Metastasis from Esophageal Carcinoma
Chapter 13: Vascular Tumors and Malformations of the Uvea
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Clinical Features
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Wide-Angle Imaging
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Effects on Adjacent Structures
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green Angiography
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Ultrasonography
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Fundus Autofluorescence
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Clinicopathologic Correlation of a Progressively Enlarging Tumor
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Clinicopathologic Correlation of a Large Tumor Simulating Choroidal Melanoma
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Laser Photocoagulation and Photodynamic Therapy
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Photodynamic Therapy
Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma: Photodynamic Therapy
Choroidal Hemangioma: Plaque Radiotherapy
Diffuse Choroidal Hemangioma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Diffuse Choroidal Hemangioma: Sturge–weber Syndrome
Diffuse Choroidal Hemangioma: Sturge–weber Syndrome
Diffuse Choroidal Hemangioma: Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Sturge–weber Syndrome
Diffuse Choroidal Hemangioma: External Beam Radiotherapy and Plaque Radiotherapy
Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis
Uveal Hemangiopericytoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Choroidal Hemangiopericytoma
Iris Vascular Tumors and Malformations
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Iris Capillary and Cavernous Hemangioma
Iris Cavernous Hemangioma: Isolated Case, and Case with Cutaneous and Central Nervous System Cavernous Hemangioma
Iris Arteriovenous Communication (Racemose Hemangioma)
Iris Varix
Chapter 14: Osseous, Myogenic, Neurogenic, Fibrous, and Histiocytic Tumors of the Uvea
Choroidal Osteoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Choroidal Osteoma: Clinical Features
Choroidal Osteoma: Wide-Angle Imaging
Choroidal Osteoma: Choroidal Neovascularization, Decalcification, and Familial Occurrence
Choroidal Osteoma: Fluorescein Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography Findings
Choroidal Osteoma: Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Clinicopathologic Correlation
Myogenic Tumors of the Uvea
Uveal Leiomyoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Uveal Leiomyoma: Clinical Variations
Uveal Leiomyoma: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Uveal Rhabdomyosarcoma
Uveal Rhabdomyosarcoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Iris and Ciliary Body Rhabdomyosarcomas
Uveal Schwannoma (Neurilemoma)
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Uveal Schwannoma (Neurilemoma)
Choroidal Melanotic Schwannoma
Uveal Neurofibroma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Other Uveal Manifestations of Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Uveal Involvement in Neurofibromatosis: Lisch Nodules and Uveal Neurofibroma
Uveal Juvenile Xanthogranuloma and Langerhans— Cell Histiocytosis
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology and Pathogenesis
Diagnostic Approaches
Management
Selected References
Iris Juvenile Xanthogranuloma: Clinical Features and Response to Treatment
Uveal Juvenile Xanthogranuloma and Langerhans’ Cell Histiocytosis
Fibrous Histiocytoma, Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor, and Other Histiocytic Tumors of the Uvea
Selected References
Miscellaneous Uveal Tumors: Fibrous Histiocytoma and Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor
Part 2: Tumors of the Retina and Optic Disc
Chapter 15: Retinoblastoma: Introduction, Genetics, Clinical Features, Classification
Retinoblastoma: Introduction, Genetics, and Clinical Features
Introduction
Genetics
Clinical Features
Spontaneous Regression
International Classification of Retinoblastoma
Selected References
Table 15.1: The international classification of retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma: Leukocoria
Retinoblastoma: Clinical Features
Retinoblastoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Small Tumors
Retinoblastoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Medium-Sized Tumors
Retinoblastoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Large Tumors
Retinoblastoma: Exophytic Growth Pattern
Retinoblastoma: Endophytic Growth Pattern
Retinoblastoma: Diffuse Growth Pattern
Retinoblastoma Presenting with Neovascular Glaucoma
Retinoblastoma Presenting as Orbital Cellulitis
Retinoblastoma: Massive Extraocular Extension
Retinoblastoma: Congenital Aggressive Type
Retinoblastoma in Older Children
Retinoblastoma: International Classification of Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma: Spontaneously Arrested and Spontaneously Regressed Tumors (Retinocytoma)
Retinoblastoma: Spontaneously Arrested and Spontaneously Regressed Tumors (Retinocytoma). Wide-Angle Imaging
Spontaneously Regressed Retinoblastoma (Retinocytoma): Malignant Transformation
Retinoblastoma: Associated with Pinealoblastoma (“Trilateral Retinoblastoma”) and Pineal Cyst Simulating Pinealoblastoma
Retinoblastoma: Association with 13Q Deletion Syndrome
Retinoblastoma: Association with Other Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chapter 16: Retinoblastoma: Diagnostic Approaches
Retinoblastoma: Diagnostic Approaches
Fluorescein Angiography
Ultrasonography
Optical Coherence Tomography
Autofluorescence
Computed Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Selected References
Retinoblastoma: Fluorescein Angiography
Retinoblastoma: Wide-Angle Fluorescein Angiography
Retinoblastoma: Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Retinoblastoma: Handheld Optical Coherence Tomography for Retinoblastoma
Chapter 17: Retinoblastoma: Pathology
Retinoblastoma: Pathology
Selected References
Retinoblastoma: Pathology, Gross Features
Retinoblastoma: Pathology and Microscopic Features
Retinoblastoma: Cavitary Variant and Clinicopathologic Correlations
Retinoblastoma: High-Risk Pathology Features
Chapter 18: Management of Retinoblastoma
Management of Retinoblastoma
General Considerations
Enucleation
External Beam Radiotherapy
Plaque Radiotherapy
Cryotherapy
Laser Photocoagulation
Transpupillary Thermotherapy
Chemotherapy
Intravenous Chemotherapy (Chemoreduction)
Intra-arterial Chemotherapy
Periocular Chemotherapy
Intravitreal Chemotherapy
Prognosis
Summary
Selected References
Retinoblastoma: Laser Photocoagulation and Cryotherapy
Retinoblastoma: External Beam Radiotherapy
Retinoblastoma: Plaque Radiotherapy
Retinoblastoma: Plaque Radiotherapy
Retinoblastoma: Plaque Radiotherapy, Wide-Angle Imaging and Tumor Regression Patterns
Retinoblastoma: Wide-Angle Imaging of Plaque Radiotherapy for Macular Recurrence of Retinoblastoma after Chemoreduction
Retinoblastoma: Plaque Radiotherapy for Tumor Recurrence after Chemoreduction
Retinoblastoma: Chemothermotherapy
Retinoblastoma: Chemoreduction in Bilateral and Unilateral Cases
Retinoblastoma: Combined Chemoreduction and Focal Thermotherapy for Macular Tumors
Retinoblastoma: Chemoreduction and Foveal-Sparing Transpupillary Thermotherapy for Macular Tumors
Retinoblastoma: Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for Primary Treatment
Retinoblastoma: Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for Secondary Treatment
Retinoblastoma: Intravenous Plus Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for Advanced Bilateral Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma: Intravitreal Chemotherapy for Vitreous Seeding
Chemoreduction, Subconjunctival Carboplatin, and External Beam Radiation for Advanced Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma: Enucleation and Harvesting of Fresh Tumor Tissue
Retinoblastoma: Appearance of Prosthesis Following Enucleation in Younger Children
Retinoblastoma: Appearance of the Prosthesis Following Enucleation in Older Children
Chapter 19: Lesions That Can Simulate Retinoblastoma
Lesions Simulating Retinoblastoma
Selected References
Table 19.1: Lesions simulating retinoblastoma (pseudoretinoblastoma) in 604 patients
Coats Disease Simulating Retinoblastoma
Advanced Coats Disease Simulating Retinoblastoma: Clinical and Fluorescein Angiographic Features
Coats Disease: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Coats Disease Causing Anterior Chamber Cholesterolosis
Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous (Persistent Fetal Vasculature)
Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous: Clinical and Pathologic Features
Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy Simulating Retinoblastoma
Ocular Toxocariasis Simulating Retinoblastoma
Endogenous Endophthalmitis Simulating Retinoblastoma
Idiopathic Intraocular Abscess with Calcification, Simulating Retinoblastoma
Incontinentia Pigmenti Simulating Retinoblastoma
Miscellaneous Conditions Simulating Retinoblastoma
Chapter 20: Vascular Tumors of the Retina and Optic Disc
Retinal Hemangioblastoma (Capillary Hemangioma)
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Retinal Hemangioblastoma
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Wide-Angle Imaging
Retinal Hemangioblastoma (Nodular) of the Optic Nerve
Retinal Hemangioblastoma (Sessile) of the Optic Nerve
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Fluorescein Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Association with Von Hippel–Lindau Syndrome
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Retinal Hemangioblastoma in Older Patients and in a Patient with Marshall–Stickler Syndrome
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Laser Photocoagulation
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Cryotherapy
Retinal Hemangioblastoma: Photodynamic Therapy
Retinal Cavernous Hemangioma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Retinal Cavernous Hemangioma: Clinical Variations
Retinal Cavernous Hemangioma: 52-Year Follow-Up and Clinicopathologic Correlation
Retinal Cavernous Hemangioma: Fluorescein Angiography
Retinal Cavernous Hemangioma with Involvement of the Optic Disc
Familial Retinal Cavernous Hemangioma Associated with Central Nervous System and Cutaneous Vascular Anomalies
Retinal Racemose Hemangioma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Retinal Racemose Hemangioma: Clinical Features
Retinal Racemose Hemangioma: Fluorescein Angiography
Retinal Racemose Hemangioma: Advanced Case with Fluorescein Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography
Retinal Racemose Hemangioma Complicated by Branch Retinal Vein Obstruction
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus. Primary Type: Clinical Features
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus. Primary Type: Wide-Angle Imaging
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus. Primary Type: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus: Secondary Type
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus: Secondary Type Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus: Treatment with Laser Photocoagulation, Cryotherapy, or Plaque Radiotherapy
Vasoproliferative Tumor of the Ocular Fundus: Treatment with Photodynamic Therapy or Cryotherapy
Chapter 21: Glial Tumors of the Retina and Optic Disc
Solitary Circumscribed Retinal Astrocytic Proliferation
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Solitary Circumscribed Retinal Astrocytic Proliferation
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma, Noncalcified Type: Clinical and Pathologic Features
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Calcified Type
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Calcified Type, Clinical and Pathologic Features
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Standard and Wide-Angle Imaging
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Fluorescein Angiography
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Optical Coherence Tomography
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Extraocular Features
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Atypical Variations
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Aggressive Tumor in Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Extraocular Extension in a Patient with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Retinal Astrocytic Hamartoma: Atypical Tumor Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Acquired Retinal Astrocytoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Acquired Retinal Astrocytoma
Acquired Retinal Astrocytoma: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Acquired Retinal Astrocytoma: Clinicopathologic Correlations
Acquired Retinal Astrocytoma: Pigmented Variants Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Acquired Retinal Astrocytoma: Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy and Management with Photodynamic Therapy
Part 3: Tumors of the Pigment Epithelium, Nonpigmented Epithelium, and Lymphoma/Leukemia
Chapter 22: Tumors and Related Lesions of the Pigment Epithelium
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Clinical Variations
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Wide-Angle Imaging of Predominantly Pigmented Lesions
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Wide-Angle Imaging of Predominantly Nonpigmented Lesions
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Fluorescein Angiography and Histopathology
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Autofluorescence and Optical Coherence Tomography Correlations
Solitary Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Documented Growth in The Basal Dimension
Multifocal Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (Congenital Grouped Pigmentation; Bear Tracks)
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Multifocal Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Hamartomas Associated with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis and Gardner Syndrome
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology and Pathogenesis
Management
Selected References
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Hamartomas Associated with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Pseudoneoplastic Reactive Hyperplasia of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Pseudoneoplastic Reactive Hyperplasia of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Hyperplasia and Migration of the Pigment Epithelium Simulating a Uveal Melanoma with Extraocular Extension
Congenital Simple Hamartoma of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Torpedo Maculopathy
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Congenital Simple Hamartoma of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium and Torpedo Maculopathy
Combined Hamartoma of the Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Combined Hamartoma of Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Juxtapapillary Type And Histopathology
Combined Hamartoma of Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Extrapapillary Type
Combined Hamartoma of Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Wide-Angle Imaging and Association with Neurofibromatosis and Brachio-Oculo-Facial Syndrome
Combined Hamartoma of Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Fluorescein Angiography
Combined Hamartoma of Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Optical Coherence Tomography Correlations
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Iris Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Iris Pigment Epithelium
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Iris and Ciliary Body Pigment Epithelium: Clinicopathologic Correlation of a Growing Lesion
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Ciliary Body Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Ciliary Body Pigment Epithelium
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Ciliary Body Pigment Epithelium with Posterior Extension into the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Benign Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Fluorescein Angiography and Ultrasonography
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of Retinal Pigment Epithelium in African-American Patients
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Simulating a Melanocytoma
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Simulating Melanoma
Epithelioma of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Simulating a Choroidal Neovascular Membrane
Malignant Epithelioma (Adenocarcinoma) of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Arising from Congenital Hypertrophy of the RPE
Malignant Epithelioma (Adenocarcinoma) of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Arising from Congenital Hypertrophy of the RPE
Presumed Epithelioma (Adenoma) of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Arising from a Laser Scar
Presumed Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Arising from an Inflammatory Scar
Malignant Epithelioma of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Aggressive Variant
Chapter 23: Tumors of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Epithelium
Congenital Neoplasms (Medulloepithelioma)
Congenital Neoplasms of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Epithelium (Intraocular Medulloepithelioma)
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Ciliary Body Medulloepithelioma: Clinical and Gross Pathologic Features
Malignant Teratoid Medulloepithelioma: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Malignant Teratoid Medulloepithelioma: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Ciliary Body Medulloepithelioma Simulating Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
Pigmented Malignant Medulloepithelioma of the Ciliary Body
Aggressive Malignant Ciliary Body Medulloepithelioma in an Adult
Medulloepithelioma of the Optic Nerve and Syndromes Related to Medulloepithelioma
Age-Related Hyperplasia of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Epithelium (Coronal Adenoma; Fuchs Adenoma)
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Diagnostic Approaches
Management
Selected References
Age-Related Hyperplasia of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium (Coronal Adenoma; Fuchs Adenoma)
Acquired Epithelioma of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Pathology
Diagnostic Approaches
Management
Selected References
Benign Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium: Clinical Features
Benign Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Benign Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium: Clinicopathologic Correlation and Treatment
Benign Epithelioma (Adenoma) of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium: Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Pleomorphic Adenocarcinoma of the Nonpigmented Ciliary Body Epithelium: Clinicopathologic Correlations
Chapter 24: Intraocular Lymphoid Tumors and Leukemias
Intraocular Lymphoid Tumors
Introduction to Intraocular Lymphoid Lesions
Selected References
Benign Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia of the Uvea
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Uveal Benign Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Uveal Benign Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia: Clinical and Pathologic Features
Uveal Benign Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Studies and Treatment
Uveal Benign Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia Masquerading as Birdshot Choroiditis or Sarcoidosis
Uveal Benign Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia: Wide-Angle Imaging, Ultrasonography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Uveal Lymphoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Uveal Lymphoma: Response to Radiotherapy
Uveal Lymphoma: Optical Coherence Tomography of Calm, Rippled or Seasick Appearance
Uveal Lymphoma: Aggressive Form
Uveal Lymphoma: Aggressive Form Presenting with Painful Secondary Glaucoma
Uveal Lymphoma: Aggressive Form with Orbital Involvement
Uveal Plasmacytoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Choroidal Plasmacytoma
Ciliary Body Plasmacytoma
Primary Vitreoretinal and Central Nervous System Lymphoma
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma
Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma: Wide-Angle Imaging and Management
Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma: Spontaneous Regression After Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
Intraocular Leukemia
General Considerations
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Approaches
Pathology
Management
Selected References
Intraocular and Optic Nerve Involvement with Leukemia
Intraocular and Optic Nerve Involvement with Leukemia: Clinicopathologic Correlation
Chapter 25: Surgical Management of Intraocular Tumors
Chapter 25: Surgical Management of Intraocular Tumors
Selected References
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: Instrumentation and Technique
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Anterior Segment Lesions
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Posterior Segment Lesions
Plaque Radiotherapy for Intraocular Tumors: Plaque Design and Application
Application Technique of the Radioactive Plaque
Application of a Radioactive Plaque for a Large Ciliochoroidal Melanoma
Application of Radioactive Plaque for an Iris Tumor
Application of Radioactive Plaque for Advanced Iris Melanoma
Removal of an Iris Tumor by Partial Iridectomy
Removal of an Iridociliary Tumor by Partial Lamellar Iridocyclectomy
Removal of a Peripheral Choroidal Tumor by Partial Lamellar Cyclochoroidectomy
Enucleation
Enucleation Implants: Standard and Coated Hydroxyapatite Implants
Enucleation Conformer and Prosthesis
Enucleation Socket and Prosthesis
Ocular Prosthesis in Young Patients Following Enucleation
Ocular Prosthesis in Adult Patients Following Enucleation
Ocular Prosthesis and Protective Polycarbonate Glasses Following Enucleation
Orbital Exenteration
Orbital Exenteration Prosthesis
Appendix
Remarks
ebookshop
| An aparitie | 2015 |
| Autor | Dr. Jerry A. Shields, Dr. Carol L. Shields |
| Dimensiuni | 21.8 x 2.3 x 28.2 cm |
| Editura | LWW |
| Format | Hardback |
| ISBN | 9781496321343 |
| Limba | Engleza |
| Nr pag | 608 |
-
1,30700 lei 1,18400 lei










Clientii ebookshop.ro nu au adaugat inca opinii pentru acest produs. Fii primul care adauga o parere, folosind formularul de mai jos.