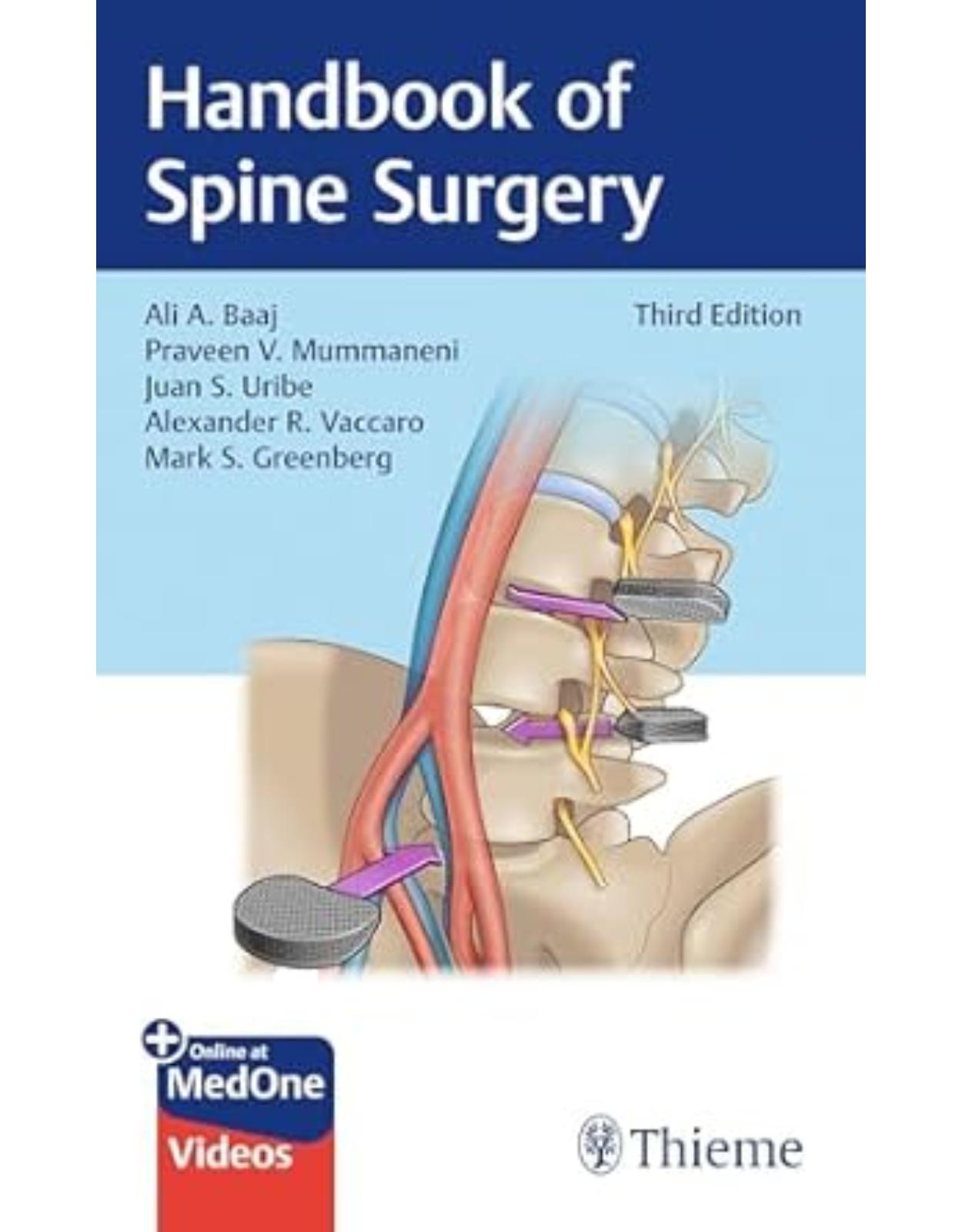
Handbook of Spine Surgery
Livrare gratis la comenzi peste 500 RON. Pentru celelalte comenzi livrarea este 20 RON.
Disponibilitate: La comanda in 4 saptamani
Editura: Thieme
Limba: Engleza
Nr. pagini: 676
Coperta: Paperback
Dimensiuni: 127 x 202 x 32 mm
An aparitie: 4 dec 2024
The go-to handbook on the current evaluation and surgical management of spinal disorders
Handbook of Spine Surgery, Third Edition edited by renowned spine surgeons Ali A. Baaj, Praveen V. Mummaneni, Juan S. Uribe, Alexander R. Vaccaro, and Mark S. Greenberg reflects new techniques introduced into the practice since publication of the last edition, along with four-color images and videos.
The book is organized into four parts and 66 chapters, starting with basic spinal anatomy. Part II covers the physical exam, electrodiagnostic testing, imaging, safety issues, intraoperative monitoring, bedside procedures, and the use of orthotics, pharmacology, and biologics. Part III discusses a full range of spinal pathologies and the final section concludes with 34 succinct procedural chapters.
Key Highlights
Contributions from an expanded "who's who" of spine surgery experts
New chapters cover state-of-the-art techniques, including endoscopy, CT-guided navigation, robotics, augmented reality, and vertebral body tethering
Procedural chapters include key points, indications, diagnosis, preoperative management, anatomic considerations, techniques, surgical pearls, and more
This is an invaluable resource for neurosurgical and orthopaedic residents, spinal surgical fellows, and practicing orthopaedic surgeons and neurosurgeons who specialize in spine surgery.
Table of Contents:
Section I Anatomy
1 Craniovertebral Junction
1.1 Key Points
1.2 Bony Anatomy
1.3 Neural Anatomy
1.4 Vascular Anatomy
1.5 Muscular Anatomy ( ▶ Table 1.1 )
1.6 Ligamentous Anatomy ( ▶ Table 1.2 )
1.7 Surgical Pearls
1.8 Common Clinical Questions
1.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
1.10 References
2 Cervical Spine
2.1 Key Points
2.2 Bony Anatomy
2.2.1 Bony Landmarks
2.2.2 Vertebrae Anatomy
2.2.3 Geometric Measurements
2.2.4 Biomechanics and Mobility
2.3 Neural Anatomy
2.3.1 Geometric Orientation
2.3.2 Cervical Plexus and Phrenic Nerve
2.3.3 Brachial Plexus
2.3.4 Sympathetic Ganglia
2.4 Vascular Anatomy
2.4.1 Vertebral Artery Segments: V1 to V4
2.4.2 Blood Supply to Spinal Cord
2.4.3 Venous Drainage
2.4.4 Transverse Foramen and the Vertebral Artery
2.5 Ligamentous and Muscular Anatomy
2.5.1 Ligamentous Anatomy
2.5.2 The Carotid Triangle
2.5.3 Muscular Anatomy
2.6 Variations in Anatomy
2.7 Surgical Pearls
2.8 Common Clinical Questions
2.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
2.10 References
3 Thoracic Spine
3.1 Key Points
3.2 Bony Anatomy ( ▶ Fig. 3.1 and ▶ Fig. 3.2) ▶ [12]
3.3 Neural Anatomy
3.4 Vascular Anatomy
3.5 Ligamentous and Muscular Anatomy ( ▶ Table 3.1 )
3.6 Surgical Pearls
3.7 Common Clinical Questions
3.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
3.9 References
4 Lumbar Spine
4.1 Key Points
4.2 Bony Anatomy
4.3 Neural Anatomy
4.4 Vascular Anatomy ( ▶ Fig. 4.4)
4.5 Ligamentous and Muscular Anatomy
4.6 Surgical Pearls
4.7 Common Clinical Questions
4.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
4.9 References
5 Sacral–Iliac Spine
5.1 Key Points
5.2 Bony Anatomy
5.3 Neural Anatomy
5.4 Vascular Anatomy
5.5 Ligamentous and Muscular Anatomy
5.6 Surgical Pearls
5.7 Common Clinical Question
5.8 Answer to Common Clinical Question
5.9 References
Section II Clinical Spine Surgery
6 Physical Examination
6.1 Key Points
6.2 Main Components of the Spinal-Related Examination
6.3 Clinical Pearls
6.4 Common Clinical Questions
6.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
6.6 References
7 Spinal Imaging
7.1 Key Points
7.2 Description
7.3 Surgical Pearls
7.4 Common Clinical Questions
7.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
7.6 References
8 Radiation Exposure in Spine Surgery
8.1 Key Points
8.2 Description
8.3 General Principles of Radiation Protection ▶ [47],▶ [52],▶ [53],▶ [54],▶ [55],▶ [56]
8.4 Evidence-Based Medicine Statements ▶ [49],▶ [55]
8.5 Surgical Pearls
8.6 Common Clinical Questions
8.7 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
8.8 References
9 Electrodiagnostic Testing in Spine Surgery
9.1 Key Points
9.2 Description
9.2.1 Nerve Conduction Study
9.2.2 Electromyogram (EMG)
9.2.3 Pathophysiology of Radiculopathy
9.3 EMG/NCS Pearls
9.4 Common Clinical Questions
9.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
9.6 References
10 Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Spine Surgery
10.1 Introduction
10.2 Key Points
10.3 Methods
10.4 Somatosensory Evoked Potentials
10.5 Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potentials
10.6 Free-Run EMG
10.7 Triggered EMG
10.8 H Reflex
10.9 Neuromonitoring in Spinal Deformity Surgery
10.10 Neuromonitoring for the Detection of Radiculopathy in Three-Column Osteotomies
10.11 Mechanomyography
10.12 Epidural D Wave Monitoring for Intradural/Intramedullary Pathology
10.13 Common Clinical Questions
10.14 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
10.15 Acknowledgments
10.16 References
11 Bedside Procedures
11.1 Key Points
11.2 Indications
11.3 Technique
11.3.1 Halo Orthosis and Traction
11.3.2 Lumbar Puncture or Lumbar Drain
11.4 Complications
11.4.1 Halo Orthosis and Traction
11.4.2 Lumbar Puncture or Lumbar Drain
11.5 Postprocedure Care
11.5.1 Halo Orthosis and Traction
11.5.2 Lumbar Puncture or Lumbar Drain
11.6 Outcomes
11.7 Surgical Pearls
11.7.1 Halo Orthosis and Traction
11.7.2 Lumbar Puncture or Lumbar Drain
11.8 Common Clinical Questions
11.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
11.10 Acknowledgments
11.11 References
12 Orthotics in Spine Surgery
12.1 Key Points
12.2 Indications
12.3 Biomechanics of Spinal Orthoses ▶ [80],▶ [81]
12.4 Classifications
12.5 Cervical Orthoses (CO)
12.6 Cervicothoracic Orthoses (CTO)
12.7 Cervicothoracolumbosacral Orthoses (CTLSO) ▶ [89]
12.8 Thoracolumbosacral Orthoses (TLSO)
12.9 Lumbosacral Orthoses (LSO)
12.10 Sacroiliac Orthoses (SIO)
12.11 Common Clinical Questions
12.12 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
12.13 References
13 Pharmacology of Antithrombotics, Antifibrinolytics, and Osteoporosis Medications
13.1 Key Points
13.2 Prophylactic Anticoagulation
13.3 Treatment of Preoperative Thromboembolic Events
13.4 Treatment of Postoperative Thromboembolic Events
13.5 Reversal of Anticoagulation ( ▶ Table 13.1 )
13.6 Antifibrinolytic Agents
13.7 Osteoporosis Medications ( ▶ Table 13.2 )
13.8 Surgical Pearls
13.9 Common Clinical Questions
13.10 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
13.11 References
14 Spine Biologics
14.1 Key Points
14.2 Introduction
14.2.1 Evolution and Market Growth
14.2.2 Basic Properties
14.3 Classification
14.4 Autologous Biologics
14.4.1 Autografts
14.4.2 Bone Marrow Aspirate
14.4.3 Growth Factors
14.5 Allogenic Biologics
14.5.1 Allografts
14.5.2 Demineralized Bone Matrix
14.5.3 Bone Morphogenetic Protein
14.5.4 Synthetic Biologics
14.6 Pediatric
14.7 BOnE Classification
14.8 MISS and Biologics
14.9 Current Developments and Trends
14.10 Surgical Pearls
14.11 Common Clinical Questions
14.12 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
14.13 References
Section III Spinal Pathology
15 Congenital Anomalies
15.1 Key Points
15.2 Vertebral Developmental Abnormalities
15.2.1 Congenital Scoliosis
15.2.2 Klippel-Feil Syndrome (KFS)
15.3 Anomalies of Notochord Formation
15.3.1 Split Cord Malformations (SCMs)
15.4 Anomalies of Dysjunction
15.4.1 Spinal Lipomas ▶ [127]
15.4.2 Myelomeningocele
15.5 Surgical Pearls
15.6 Common Clinical Questions
15.7 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
15.8 References
16 Cervical Trauma
16.1 Key Points
16.2 General Principles
16.3 Upper Cervical Spine Trauma
16.3.1 Atlantooccipital Dissociation
16.3.2 Atlas (C1) Fracture
16.3.3 Axis (C2) Fracture and Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of C2 (Hangman’s Fracture)
16.3.4 Dens Fracture (C2)
16.3.5 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma (C3–C7)
16.4 Common Clinical Questions
16.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
16.6 References
17 Thoracolumbar Trauma
17.1 Key Points
17.2 General Principles
17.3 Thoracolumbar Fracture
17.3.1 Key Concepts
17.4 Bracing
17.5 Conus Medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes
17.6 Spinal and Neurogenic Shock
17.7 Common Clinical Questions
17.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
17.9 References
18 Sacropelvic Trauma
18.1 Key Points
18.2 Sacral Fractures
18.2.1 Background
18.2.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
18.2.3 Workup
18.2.4 Neuroimaging
18.2.5 Treatment
18.2.6 Surgical Pearls
18.3 Type B Injuries
18.3.1 Background
18.3.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
18.3.3 Workup
18.3.4 Neuroimaging
18.3.5 Treatment
18.3.6 Surgical Pearls
18.4 Type C Injuries
18.4.1 Background
18.4.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
18.4.3 Workup
18.4.4 Neuroimaging
18.4.5 Treatment
18.4.6 Surgical Pearls
18.5 Traumatic Spinopelvic Dissociations (Type C3 Injuries)
18.5.1 Background
18.5.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
18.5.3 Workup
18.5.4 Neuroimaging
18.5.5 Treatment
18.5.6 Surgical Pearls
18.6 Common Clinical Questions
18.7 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
18.8 References
19 Infection
19.1 Key Points
19.2 Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis and Diskitis ▶ [184],▶ [185],▶ [186]
19.2.1 Etiology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenesis
19.2.2 Patient Presentation
19.2.3 Diagnostic Workup
19.2.4 Treatment
19.2.5 Prognosis/Complications
19.3 Epidural Infections ▶ [187],▶ [188]
19.3.1 Etiology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenesis
19.3.2 Patient Presentation
19.3.3 Diagnostic Workup
19.3.4 Treatment
19.3.5 Prognosis/Complications
19.4 Intradural Infections ▶ [189],▶ [190]
19.4.1 Etiology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenesis
19.4.2 Patient Presentation
19.4.3 Diagnostic Workup
19.4.4 Treatment
19.4.5 Prognosis/Complications
19.5 Postoperative Infections ▶ [191],▶ [192],▶ [193],▶ [194]
19.5.1 Etiology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenesis
19.5.2 Prophylaxis
19.5.3 Patient Presentation
19.5.4 Diagnostic Workup
19.5.5 Treatment
19.5.6 Prognosis/Complications
19.6 Surgical Pearls
19.7 Common Clinical Questions
19.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
19.9 References
20 Primary Bony Spinal Column Tumors
20.1 Key Points
20.2 Background
20.3 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
20.4 Workup and Neuroimaging
20.5 Treatment
20.6 Surgical Pearls
20.7 Common Clinical Question
20.8 Answer to Common Clinical Question
20.9 References
21 Surgical Management of Spinal Metastases
21.1 Key Points
21.2 Background
21.3 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
21.4 Workup and Neuroimaging
21.5 Treatment
21.6 Surgical Pearls
21.7 Common Clinical Questions
21.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
21.9 References
22 Intradural Extramedullary and Intramedullary Spinal Tumors
22.1 Key Points
22.2 Indications
22.3 Technique
22.3.1 Surgical Technique for Intradural Extramedullary Tumors
22.3.2 Surgical Technique for Intradural Intramedullary Tumors
22.4 Complications
22.5 Postoperative Care
22.6 Surgical Pearls
22.7 Outcomes
22.8 Common Clinical Questions
22.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
22.10 References
23 Cervical and Thoracic Spine Degenerative Disease
23.1 Key Points
23.2 Cervical Disk Herniation
23.2.1 Background
23.2.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
23.2.3 Workup
23.2.4 Treatment
23.2.5 Surgical Pearls
23.3 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
23.3.1 Background
23.3.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
23.3.3 Workup
23.3.4 Treatment
23.3.5 Surgical Pearls
23.4 Common Clinical Questions
23.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
23.6 References
24 Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease
24.1 Key Points
24.2 Background
24.3 Specific Conditions
24.3.1 Radicular Pain
24.3.2 Neurogenic Claudication
24.3.3 Axial Back Pain from Intervertebral Disk Disease (without Deformity)
24.3.4 Axial Back Pain from Facet Joint Disease
24.3.5 Spondylolisthesis
24.3.6 Degenerative Scoliosis and Kyphosis
24.4 Common Clinical Questions
24.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
24.6 References
25 Congenital and Neuromuscular Scoliosis
25.1 Key Points
25.2 Congenital Scoliosis
25.3 Neuromuscular Scoliosis
25.4 Common Clinical Questions
25.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
25.6 References
26 Scheuermann’s Kyphosis
26.1 Key Points
26.2 Background
26.3 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
26.4 Workup
26.5 Neuroimaging
26.6 Treatment
26.6.1 Nonoperative Treatment
26.6.2 Operative Treatment
26.7 Surgical Pearls
26.8 Common Clinical Questions
26.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
26.10 References
27 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
27.1 Key Points
27.2 Definition
27.3 Prevalence
27.4 Clinical Evaluation
27.5 Radiographic Evaluation
27.6 Skeletal Maturity
27.7 Management Overview
27.8 Observation
27.9 Bracing
27.10 Physical Therapy
27.11 Surgical Intervention
27.12 Lenke Classification
27.13 Instrumented Level Selection
27.14 Common Clinical Questions
27.15 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
27.16 References
28 Adult Degenerative Deformity
28.1 Key Points
28.2 Background
28.3 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
28.4 Evaluation of Adult Degenerative Deformity
28.5 Spinopelvic Parameters
28.6 Treatment
28.7 Complications
28.8 Common Clinical Questions
28.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
28.10 References
29 Radiographic Parameters of Spinal Deformity
29.1 Key Points
29.2 Background
29.3 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
29.3.1 Neuroimaging
29.4 Treatment
29.5 Common Clinical Questions
29.6 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
29.7 References
30 Vascular Pathology of the Spine
30.1 Key Points
30.2 Cavernous Malformations
30.3 Arteriovenous Lesions
30.4 Common Clinical Questions
30.5 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
30.6 References
31 Spondyloarthropathies
31.1 Key Points
31.2 Ankylosing Spondylitis Seronegative Arthropathy
31.2.1 Background
31.2.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
31.2.3 Workup
31.2.4 Neuroimaging
31.2.5 Treatment
31.2.6 Surgical Pearls
31.3 Rheumatoid Arthritis
31.3.1 Background
31.3.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
31.3.3 Workup
31.3.4 Neuroimaging
31.3.5 Treatment
31.3.6 Surgical Pearls
31.4 Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
31.4.1 Background
31.4.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
31.4.3 Workup/Neuroimaging
31.4.4 Treatment
31.4.5 Surgical Pearls
31.5 Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
31.5.1 Background
31.5.2 Signs, Symptoms, and Physical Examination
31.5.3 Workup/Neuroimaging
31.5.4 Treatment
31.5.5 Surgical Pearls
31.6 Common Clinical Questions
31.7 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
31.8 References
32 Spinal Emergencies
32.1 Key Points
32.2 Spinal Hematomas
32.3 Cauda Equina and Conus Medullaris Syndromes
32.4 Spinal Epidural Abscess
32.5 Common Clinical Questions
32.6 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
32.7 References
Section IV Surgical Techniques
33 Occipitocervical Fusion
33.1 Key Points
33.2 Indications
33.3 Technique
33.4 Complications ▶ [422],▶ [423]
33.5 Postoperative Care
33.6 Outcomes ▶ [424]
33.7 Surgical Pearls
33.8 Common Clinical Questions
33.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
33.10 References
34 Transoral Odontoidectomy
34.1 Key Points
34.2 Indications
34.3 Technique
34.4 Complications
34.5 Postoperative Care
34.6 Outcomes
34.7 Surgical Pearls
34.8 Common Clinical Questions
34.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
34.10 References
35 Endoscopic Endonasal Odontoidectomy
35.1 Key Points
35.2 Indications
35.3 Technique
35.4 Complications
35.5 Postoperative Care
35.6 Outcomes
35.7 Surgical Pearls
35.8 Common Clinical Questions
35.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
35.10 References
36 C1–C2 Fixation Techniques
36.1 Key Points
36.2 Indications of C1–C2 Fixation
36.3 Preparation for C1–C2 Fixation
36.3.1 C1–C2 Fixation Constructs Using C1 Lateral Mass Screws with C2 Pars, Pedicle, or Translaminar Screws ▶ [442],▶ [443],▶ [444],▶ [445]
36.3.2 C1–C2 Transarticular Screws ▶ [449]
36.3.3 C1–C2 Wiring Methods ▶ [444],▶ [450]
36.4 Complications
36.5 Postoperative Care
36.6 Surgical Pearls
36.7 Common Clinical Questions
36.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
36.9 References
37 Odontoid Screw Fixation
37.1 Key Points
37.2 Indications and Contraindications
37.3 Technique
37.4 Complications
37.5 Postoperative Care
37.6 Outcomes
37.7 Surgical Pearls
37.8 Common Clinical Questions
37.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
37.10 References
38 Cervical Arthroplasty
38.1 Key Points
38.2 Indications ▶ [455]
38.3 Technique
38.4 Complications ▶ [457]
38.5 Postoperative Care
38.6 Outcomes
38.7 Surgical Pearls
38.8 Common Clinical Questions
38.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
38.10 References
39 Anterior Cervical Diskectomy
39.1 Key Points
39.2 Indications
39.3 Technique ▶ [467],▶ [468]
39.4 Complications
39.5 Postoperative Care
39.6 Outcomes ▶ [473]
39.7 Surgical Pearls
39.8 Common Clinical Questions
39.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
39.10 References
40 Anterior Cervical Corpectomy
40.1 Key Points
40.2 Indications
40.3 Technique
40.4 Complications
40.5 Postoperative Care
40.6 Outcomes
40.7 Surgical Pearls
40.8 Common Clinical Questions
40.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
40.10 References
41 Cervical Laminectomy with and without Fusion
41.1 Key Points
41.2 Indications
41.3 Contraindications
41.4 Technique
41.5 Complications
41.6 Postoperative Care
41.7 Outcomes
41.8 Surgical Pearls
41.9 Common Clinical Questions
41.10 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
41.11 References
42 Cervical Laminoplasty
42.1 Key Points
42.2 Indications
42.3 Contraindications
42.4 Technique
42.5 Complications
42.6 Postoperative Care
42.7 Outcomes
42.8 Surgical Pearls
42.9 Common Clinical Questions
42.10 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
42.11 References
43 Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy
43.1 Key Points
43.2 Indications and Contraindications
43.2.1 Indications
43.2.2 Contraindications
43.3 Technique
43.3.1 Patient Positioning
43.3.2 Preparation and Draping
43.3.3 Surgical Techniques
43.4 Microsurgical Techniques
43.4.1 Open Microscopic Procedure
43.4.2 Tubular Retractor Procedure
43.5 Foraminotomy Under Microscope
43.6 Endoscopic Techniques
43.6.1 Full Endoscopic Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy
43.7 Biportal Endoscopic Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy
43.8 Endoscopic Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy—Destandau’s Technique
43.9 Complications of Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy
43.10 Postoperative Care
43.11 Outcomes
43.12 Surgical Pearls
43.13 Common Clinical Questions
43.14 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
43.15 Acknowledgments
43.16 References
44 Cervical Open Reduction Techniques: Anterior and Posterior Approaches
44.1 Key Points
44.2 Indications
44.3 Technique
44.3.1 Anterior Approach ▶ [528]
44.3.2 Posterior Approach
44.4 Complications
44.5 Postoperative Care
44.6 Outcomes
44.7 Surgical Pearls
44.8 Common Clinical Questions
44.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
44.10 References
45 Surgical Resection of Spinal Vascular Lesions
45.1 Key Points
45.2 Indications
45.3 Technique
45.4 Complications
45.5 Postoperative Care
45.6 Outcomes
45.7 Surgical Pearls
45.8 Common Clinical Questions
45.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
45.10 References
46 Freehand Thoracic Pedicle Screw Insertion
46.1 Key Points
46.2 Indications
46.3 Technique
46.4 Freehand Screws for Deformity: Special Considerations
46.5 Complications
46.6 Postoperative Care
46.7 Outcomes
46.8 Surgical Pearls
46.9 Common Clinical Questions
46.10 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
46.11 References
47 Navigation in Spine Surgery
47.1 Key Points
47.2 Description
47.3 Indications and Advantages
47.4 Future of Spinal Navigation
47.5 Surgical Pearls
47.6 Common Clinical Questions
47.7 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
47.8 References
48 Robotics in Spine Surgery
48.1 Key Points
48.2 Indications
48.3 Technique
48.4 Complications
48.5 Postoperative Care
48.6 Outcomes
48.7 Surgical Pearls
48.8 Common Clinical Questions
48.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
48.10 References
49 Posterolateral Thoracic Approaches
49.1 Key Points
49.2 Indications
49.3 Technique
49.3.1 Transpedicular Approach
49.3.2 Costotransversectomy
49.3.3 Lateral Extracavitary Approach
49.4 Complications
49.5 Postoperative Care
49.6 Outcomes
49.7 Surgical Pearls
49.8 Common Clinical Questions
49.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
49.10 Acknowledgments
49.11 References
50 Minimally Invasive Lateral Retropleural Approach for Thoracic Diskectomy
50.1 Key Points
50.2 Indications
50.3 Technique
50.4 Complications
50.5 Postoperative Care
50.6 Outcomes
50.7 Surgical Pearls
50.8 Common Clinical Questions
50.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
50.10 References
51 Lateral Approaches to the Thoracolumbar Spine
51.1 Key Points
51.2 Indications
51.3 Technique
51.4 Complications
51.5 Postoperative Care
51.6 Outcomes
51.7 Surgical Pearls
51.8 Common Clinical Questions
51.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
51.10 References
52 Open and Minimally Invasive Spinal Lumbar Microdiskectomy
52.1 Key Points
52.2 Indications
52.3 Technique
52.3.1 Open
52.3.2 Minimally Invasive Technique
52.4 Complications
52.5 Postoperative Care
52.6 Outcomes
52.7 Surgical Pearls
52.8 Common Clinical Questions
52.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
52.10 References
53 Lumbar Laminectomy
53.1 Key Points
53.2 Indications
53.3 Technique
53.4 Complications
53.5 Postoperative Care
53.6 Outcomes
53.7 Surgical Pearls
53.8 Common Clinical Questions
53.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
53.10 Acknowledgments
53.11 References
54 Endoscopic Lumbar Techniques
54.1 Key Points
54.2 Indications
54.3 Surgical Technique
54.4 Complications
54.5 Postoperative Care
54.6 Outcomes
54.7 Surgical Pearls
54.8 Common Clinical Questions
54.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
55 Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
55.1 Key Points
55.2 Indications
55.3 Technique
55.3.1 Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
55.4 Complications
55.5 Postoperative Care
55.6 Outcomes
55.7 Surgical Pearls
55.8 Common Clinical Questions
55.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
55.10 References
56 Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
56.1 Key Points
56.2 Indications
56.3 Technique
56.4 Complications
56.5 Postoperative Care
56.6 Outcomes
56.7 Surgical Pearls
56.8 Common Clinical Questions
56.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
56.10 Acknowledgments
56.11 References
57 Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion
57.1 Key Points
57.2 Indications ▶ [631]
57.3 Contraindications
57.4 Preoperative Planning
57.5 Patient Positioning
57.5.1 Standard LLIF
57.5.2 Prone Lateral (PL) LLIF
57.5.3 Prone Transpsoas (PTP) LLIF
57.6 Technique
57.7 Complications
57.8 Postoperative Care
57.9 Outcomes
57.10 Surgical Pearls
57.11 Common Clinical Questions
57.12 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
57.13 References
58 Single-Position Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion
58.1 Key Points
58.2 Indications
58.3 Technique
58.4 Complications
58.5 Postoperative Care
58.6 Outcomes
58.7 Surgical Pearls
58.8 Common Clinical Questions
58.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
58.10 References
59 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy/Smith-Petersen Osteotomy
59.1 Key Points
59.2 Indications
59.3 Technique
59.3.1 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy
59.3.2 Smith-Petersen Osteotomy
59.4 Complications
59.5 Postoperative Care
59.6 Outcomes
59.7 Surgical Pearls
59.8 Common Clinical Questions
59.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
59.10 References
60 Vertebral Body Tethering for Scoliosis
60.1 Key Points
60.2 Indications
60.3 Surgical Technique
60.4 Complications
60.5 Postoperative Care
60.6 Outcomes
60.7 Surgical Pearls
60.8 Common Clinical Questions
60.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
60.10 References
61 Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement
61.1 Key Points
61.2 Indications
61.3 Technique
61.4 Complications
61.5 Postoperative Care
61.6 Surgical Pearls
61.7 Common Clinical Questions
61.8 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
61.9 References
62 Awake Spine Surgery
62.1 Key Points
62.2 Indications
62.3 Technique
62.4 Complications
62.5 Postoperative Care
62.6 Outcomes
62.7 Surgical Pearls
62.8 Common Clinical Questions
62.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
62.10 References
63 Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
63.1 Advantages
63.2 Indications
63.3 Preoperative Imaging Considerations
63.4 Technique
63.5 Complications ▶ [684]
63.6 Patient-Specific Considerations
63.7 Outcomes ▶ [685]
63.8 Surgical Pearls
63.9 Common Clinical Questions
63.10 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
63.11 Acknowledgment
63.12 References
64 Sacroiliac Joint Fusion
64.1 Key Points
64.2 Indications
64.3 Techniques ( ▶ Fig. 64.1)
64.4 Complications
64.5 Postoperative Care
64.5.1 Open Technique
64.5.2 Minimally Invasive Technique
64.6 Outcomes
64.7 Surgical Pearls
64.8 Common Clinical Questions
64.9 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
64.10 References
65 Sacrectomy
65.1 Key Points
65.2 Indications
65.3 Preoperative Considerations/ Management
65.4 Anatomic Considerations
65.5 Technique
65.5.1 Combined Anterior–Posterior Approach
65.5.2 Reconstruction
65.6 Complications
65.7 Postoperative Care
65.8 Outcomes
65.9 Surgical Pearls
65.10 Common Clinical Questions
65.11 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
65.12 References
66 Vertebral Body Augmentation
66.1 Key Points
66.2 Indications
66.3 Diagnosis
66.4 Technique
66.4.1 Vertebroplasty
66.4.2 Kyphoplasty
66.5 Complications
66.6 Postoperative Care
66.7 Outcomes
66.8 Surgical Pearls
66.9 Common Clinical Questions
66.10 Answers to Common Clinical Questions
66.11 References
| An aparitie | 4 dec 2024 |
| Autor | Ali A. Baaj, Praveen Mummaneni, Juan S. Uribe, Alexander R. Vaccaro, Mark S. Greenberg |
| Dimensiuni | 127 x 202 x 32 mm |
| Editura | Thieme |
| Format | Paperback |
| ISBN | 9781684205547 |
| Limba | Engleza |
| Nr pag | 676 |
-
56200 lei 49500 lei
-
2,41000 lei 2,10000 lei
-
57800 lei 52000 lei








Clientii ebookshop.ro nu au adaugat inca opinii pentru acest produs. Fii primul care adauga o parere, folosind formularul de mai jos.