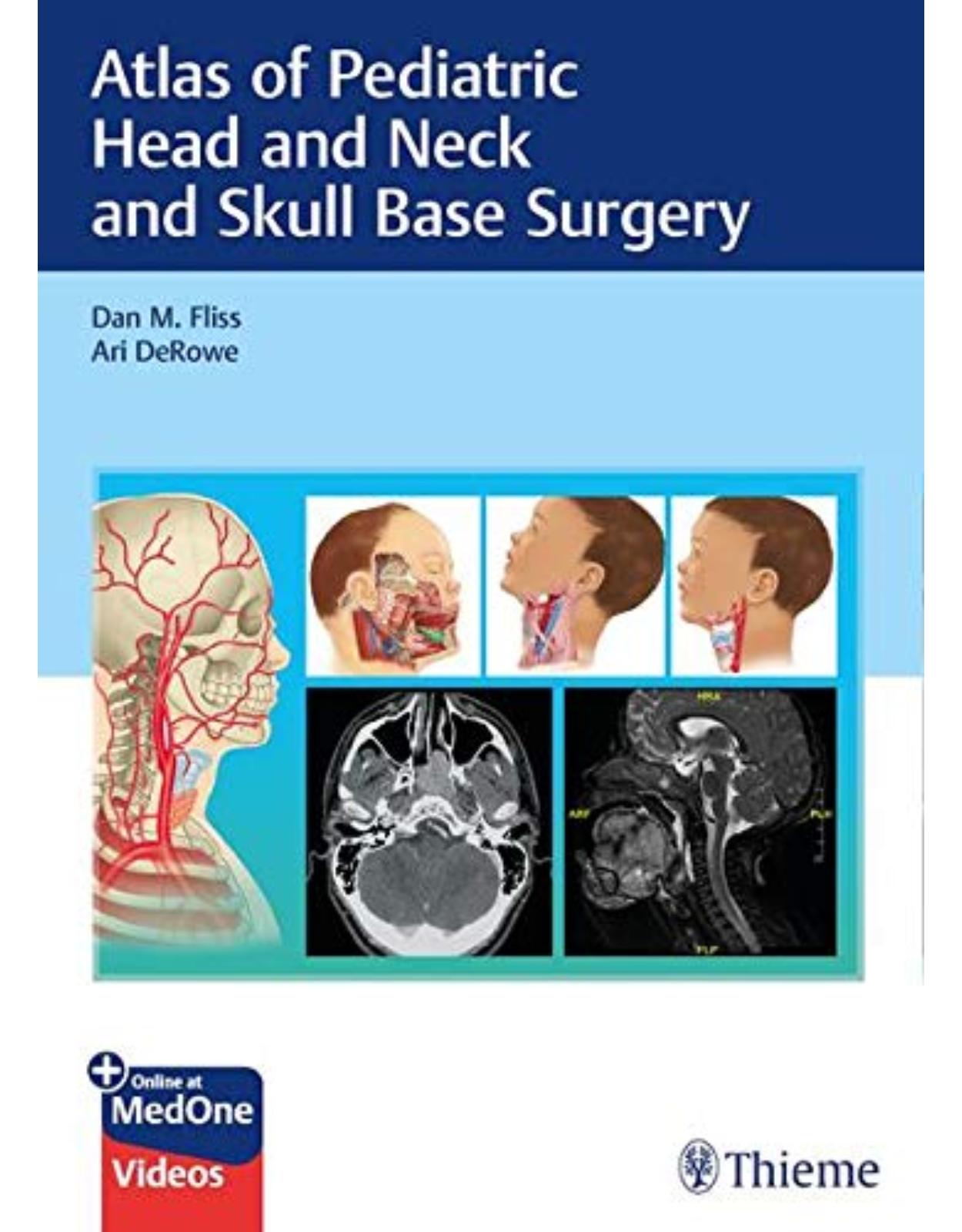
Atlas of Pediatric Head and Neck and Skull Base Surgery
Livrare gratis la comenzi peste 500 RON. Pentru celelalte comenzi livrarea este 20 RON.
Disponibilitate: La comanda in aproximativ 4-6 saptamani
Autor: Dan M. Fliss, Ari DeRowe
Editura: Thieme
Limba: Engleza
Nr. pagini: 617
Coperta: Hardcover
Dimensiuni: 26.92 x 19.56 cm
An aparitie: 9 Dec. 2020
Description:
A state-of-the-art resource on head, neck, and skull base surgical procedures in children
Pediatric otolaryngology is a rapidly expanding field with remarkable technological advances that have improved the quality of life for young patients. Many highly complex pediatric head and neck procedures are not commonly performed, resulting in a paucity of resources. Atlas of Pediatric Head and Neck and Skull Base Surgery by renowned surgeons Dan M. Fliss, Ari DeRowe, and an impressive group of interdisciplinary innovators fills a gap in the literature. The richly illustrated atlas features a detailed discussion and guidance on groundbreaking surgeries developed and currently performed by top academic surgeons in the field, many of whom contributed to this book.
The introductory section lays a solid foundation of knowledge, with discussion of pediatric anatomy, distinctive topography of the skull base, anesthesia and pain control considerations, and imaging modalities. Fifty-four subsequent chapters encompass a rich spectrum of approaches and pediatric pathologies, organized by head and neck; skull base and craniofacial; airway, voice, and swallowing; trauma; and reconstruction sections. Surgical chapters include an introduction; evidence-based guidelines; preoperative, anesthetic, intraoperative and postoperative considerations; techniques and positioning; extensive references; and more.
Key Features
Concise, targeted descriptions of preoperative, perioperative, and postoperative considerations enhance the ability to deliver high-quality surgical care and achieve optimal outcomes
Bulleted list of highlights at the end of each surgical chapter provide a quick reference
Detailed, high-quality color illustrations and surgical photographs enhance understanding of impacted anatomy and techniques
This is an essential reference for otolaryngology, maxillofacial, plastic reconstructive, and neurosurgery residents, as well as for pediatric otolaryngology and head and neck fellows. Practicing head and neck surgeons and pediatric otolaryngologists will also find it beneficial.
Table of Contents:
Section I Introduction
1 Pediatric Anatomy
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Fasciae of the Neck
1.3 Muscles of the Neck
1.3.1 Superficial Muscles
1.3.2 Middle Muscles or Muscles of the Hyoid Bone
1.3.3 Deep Muscles
1.4 Topography of the Neck
1.4.1 Muscles of the Head
1.4.2 Muscles of Mastication
1.4.3 Blood Supply of the Head and Neck
1.5 Major Salivary Glands
1.6 The Larynx
1.6.1 Cartilages of the Larynx
1.6.2 Ligaments and Membranes of the Larynx
1.6.3 Muscles of the Larynx
1.6.4 Anatomical Differences Between Pediatric and Adult Larynx
1.7 Facial Nerve
1.7.1 Components and Branches
1.8 The Organ of Hearing
1.8.1 The External Ear
1.8.2 The Tympanic Membrane
1.8.3 The Middle Ear
1.8.4 The Inner Ear
1.9 Thyroid Gland
2 The Distinctive Anatomical Features of the Pediatric Skull Base
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Cranial Fossae
2.3 Anterior Skull Base
2.4 Paranasal Sinus Development
2.5 Maxillary Sinus Development
2.6 Ethmoid Sinus Development
2.7 Frontal Sinus Development
2.8 Sphenoid Sinus Development
2.9 Lateral Skull Base
2.10 The External Auditory Canal
2.11 The Tympanic Membrane
2.12 The Middle Ear Cleft
2.13 Highlights
3 Special Considerations in Pediatric Anesthesia and Pain Control
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Perioperative Considerations
3.2.1 Airway Risks versus Safety
3.2.2 Detriments in the ENT Pediatric Population
3.3 Perioperative Anesthesia Considerations in the ENT Child
3.3.1 Preoperative Evaluation and Preparation for Anesthesia
3.3.2 Trauma Patients
3.3.3 Intraoperative Anesthesia and Analgesia Regimens
3.3.4 Postoperative Patient-Tailored Management
3.3.5 Postoperative Complications
3.4 Pain Management in ENT-Operated Children
3.4.1 Pain Handling Highlights
3.4.2 Pain Assessment
3.4.3 Specific Pain Assessment Tools
3.4.4 Analgesia Modus Operandi
3.4.5 The WHO’s Two-Step Pain Strategy
3.4.6 Late Pain Control
3.5 Conclusion
4 Imaging of the Pediatric Head and Neck
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Pediatric Imaging Safety
4.2.1 Radiation Safety
4.2.2 Sedation
4.3 The Imaging Modalities
4.3.1 Ultrasound
4.3.2 Cross-sectional Imaging
4.3.3 Radiography and Fluoroscopy
4.3.4 Nuclear Medicine
4.4 The Imaging Diagnostic Workup
Section II Head and Neck
5 Surgery of Head and Neck Infection
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Anatomy
5.3 Clinical Presentation and Preoperative Evaluation
5.4 Pathogens
5.5 Treatment
5.6 Site-Specific Surgical Technique
5.6.1 Retropharyngeal Infection
5.6.2 Parapharyngeal Space (Lateral Pharyngeal Space)
5.6.3 Peritonsillar Abscess
5.6.4 Atypical Mycobacterium
5.7 Conclusion
5.8 Highlights
6 Thyroidectomy
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Preoperative Evaluation
6.3 Outcomes
6.4 Multidisciplinary Team
6.5 Pediatric Anesthesia for Thyroidectomy
6.6 Surgical Technique/Operative Planning
6.6.1 Goals
6.6.2 Anesthesia
6.6.3 Preparation/Planning the Incision
6.6.4 Incision and Flap Elevation
6.6.5 Mobilization of Thyroid Gland
6.6.6 Key Maneuvers
6.6.7 Identifying the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve and Parathyroid Glands
6.6.8 Medialization of Thyroid Gland over Trachea
6.6.9 Removal of the Specimen, Reimplantation, and Re-evaluation of Nerves
6.6.10 Closure of Wound
6.7 Postoperative Management
6.8 Conclusion
6.9 Highlights
7 Neck Dissection for Thyroid Cancer in Children
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Guidelines for Pediatric Neck Dissection in Thyroid Malignancy
7.3 Anatomy of a Neck Dissection
7.4 Considerations for Neck Dissection in the Pediatric Population
7.5 Intraoperative Considerations
7.6 Postoperative Considerations
7.7 Surgical Technique
7.7.1 Central Neck Dissection
7.7.2 Lateral Neck Dissection
7.7.3 Postoperative Surveillance
7.7.4 Parathyroid Autoimplantation
7.8 Conclusion
7.9 Highlights
8 Pediatric Parotidectomy
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Anatomy and Embryology
8.3 Patient Evaluation
8.3.1 History and Physical Examination
8.3.2 Laboratory Evaluation
8.3.3 Imaging Studies
8.3.4 Sialendoscopy
8.3.5 Pediatric Parotid Gland Disorders
8.3.6 Congenital Lesions
8.3.7 Acquired Lesions
8.3.8 Infectious Conditions
8.3.9 Inflammatory and Autoimmune Conditions
8.4 Parotidectomy
8.4.1 Procedure
8.4.2 Postoperative Management
8.4.3 Complications
8.5 Conclusion
8.6 Highlights
9 Parapharyngeal Space Surgery in the Pediatric Population
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Infectious Disease of the PPS
9.2.1 Preoperative Evaluation
9.2.2 Surgical Technique
9.2.3 Postoperative Treatment
9.3 Parapharyngeal Space Tumors in the Pediatric Population
9.3.1 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
9.3.2 Surgical Technique
9.4 Postoperative Treatment
10 Submandibular Gland Excision
10.1 Surgical Anatomy
10.2 Preoperative Evaluation
10.3 Surgical Approaches
10.3.1 Transcervical Approach
10.3.2 Intraoral Approach
10.3.3 Endoscopic Approach
10.3.4 Complications
10.4 Postoperative Management
10.4.1 Pearls to Avoid Intraoperative Complications
10.5 Highlights
11 Pediatric Endoscopic Salivary Gland Surgery
11.1 Introduction
11.2 General Anatomical Considerations
11.3 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
11.3.1 Clinical Evaluation
11.4 Salivary Imaging
11.4.1 Submandibular Gland
11.4.2 Parotid Gland
11.4.3 Magnetic Resonance Sialography
11.5 The Thallium Scan for All Salivary Glands
11.6 Laboratory Data
11.7 Sialoendoscopy
11.8 Pediatric Anesthesia
11.9 Differential Diagnostics with Rare Nonsurgical Conditions
11.10 Surgical Technique
11.10.1 Irrigation
11.10.2 Sialoendoscopic Sialolithotomy
11.11 Combination of ESWL and Sialoendoscopic Approach
11.12 The Author’s Approaches to Various Cases
11.12.1 Surgical Approach to Specific Disorders
11.12.2 Location Statistics
11.12.3 Acute Suppurative Parotitis
11.13 The Sjögren’s Syndrome
11.13.1 Postoperative Treatment
11.14 Highlights
12 Salivary Gland Ductal Diversion, Botulinum Toxin Injection, and Salivary Ductal Ligation
12.1 Pathophysiology of Drooling and Surgical Anatomy
12.2 Mechanism of Action of Botulinum Toxin
12.3 Preoperative Evaluation
12.3.1 Clinical Evaluation
12.3.2 Anesthetic Considerations
12.4 Other Investigations
12.5 Treatment Options for Sialorrhea
12.6 Surgical Options
12.7 Operative Techniques
12.7.1 Salivary Diversion Procedures
12.7.2 Salivary Reduction Procedures
12.7.3 Submandibular Duct Ligation
12.8 Botulinum Toxin Injection in the Salivary Glands
12.9 Conclusion
12.10 Highlights
13 Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Excision
13.1 Introduction
13.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
13.3 Surgical Technique—Sistrunk Procedure
13.4 Surgical Technique—Revision
13.5 Postoperative Treatment
13.6 Complications
13.7 Highlights
14 Branchial Cleft Anomalies, Sinuses, and Cysts
14.1 Introduction
14.2 First Branchial Cleft Anomalies
14.2.1 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
14.2.2 Surgical Technique
14.2.3 Postoperative Treatment
14.2.4 Complications
14.3 Second Branchial Cleft Anomalies
14.3.1 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
14.3.2 Surgical Technique
14.3.3 Postoperative Treatment
14.3.4 Complications
14.4 Pyriform Fossa Anomalies (Formerly Third and Fourth Branchial Cleft Anomalies)
14.4.1 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
14.4.2 Surgical Technique
14.4.3 Postoperative Treatment
14.4.4 Complications
14.5 Highlights
15 Preauricular Anomalies
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
15.3 Surgical Technique
15.4 Postoperative Treatment
15.5 Highlights
16 Surgery for Lymphatic Vascular Malformations
16.1 Introduction
16.2 Hemangiomas
16.3 Vascular Malformations
16.4 Surgery for Neck Disease
16.5 Preoperative Investigations
16.6 Preoperative Considerations
16.7 Contraindications and Risks
16.8 Anesthesia
16.9 Operative Technique
16.10 Postoperative Management
16.11 Evidence-based Management
16.12 Lymphatic Malformations of the Tongue and Floor of Mouth
16.13 Highlights
17 Cervical Lymph Node Biopsy in Children
17.1 Introduction
17.2 Preoperative and Anesthesia Considerations
17.2.1 History
17.2.2 Physical Examination
17.2.3 Laboratory Studies
17.2.4 Imaging Studies
17.2.5 Needle Biopsy
17.2.6 Final Presurgical Preparations
17.3 Surgical Technique for Lymph Node Biopsy of Level III
17.3.1 Skin Incision
17.3.2 Elevation of Subplatysmal Flaps
17.3.3 Dissection along the Lymph Node in Level III
17.4 Postoperative Treatment
17.5 Highlights
18 Pediatric Maxillectomy
18.1 Introduction
18.2 Surgical Approach to Pediatric Maxillectomy
18.2.1 Midfacial Degloving
18.2.2 Combined Approach
18.2.3 Hemi–degloving
18.3 Endoscopic Maxillectomy
18.4 Highlights
19 Vagal Nerve Stimulation
19.1 Introduction
19.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
19.3 Surgical Technique
19.4 Postoperative Treatment
19.5 Highlights
20 Pediatric Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation
20.1 Introduction
20.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
20.3 Surgical Technique
20.3.1 Incision Placement and Preparation
20.3.2 EMG Monitoring
20.3.3 Preparation
20.3.4 Sensing Lead Placement
20.3.5 Impulse Generator Pocket Placement
20.3.6 Sensing Lead Placement
20.3.7 Lead Tunneling
20.3.8 Impulse Generator Placement
20.3.9 Device Testing
20.3.10 Wound Closure
20.3.11 Postoperative Treatment
20.4 Highlights
21 Lingual Tonsillectomy
21.1 Introduction
21.2 Indications for Surgery
21.3 Surgical Technique
21.4 Avoiding Complications
21.5 Postoperative Care
21.6 Highlights
22 Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
22.1 Introduction
22.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
22.3 Surgical Technique
22.3.1 Adenoidectomy
22.3.2 Complete Tonsillectomy
22.3.3 Powered Intracapsular Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
22.4 Postoperative Treatment
22.5 Highlights
23 Pediatric Transoral Robotic Surgery
23.1 Introduction
23.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
23.3 Exposure, Setup, and Instrumentation
23.4 Select Cases in Pediatric Robotic Surgery
23.4.1 Laryngeal Cleft Repair
23.4.2 Supraglottoplasty: Epiglottopexy
23.4.3 Expansion Laryngotracheoplasty with a Posterior Cricoid Graft
23.4.4 Laryngeal Cyst Excision
23.4.5 Pharyngeal Lymphatic Malformation Excision
23.4.6 Scar Band Lysis and Flaps
23.5 Postoperative Treatment
23.6 Highlights
Section III Skull Base and Craniofacial
24 Management of Periorbital Abscess
24.1 Prevalence and Pathophysiology of Periorbital and Orbital Complications of Sinusitis
24.2 Classification
24.3 Microbiology of Orbital Complications Associated with Sinusitis
24.4 Imaging Role in the Management of Orbital Complications of Sinusitis
24.5 Systemic Antibiotic Treatment vs. Surgery—When to Treat Conservatively?
24.6 Endoscopic versus Open Surgical Approach
24.7 Highlights
25 Orbital Surgery for Tumors
25.1 Introduction
25.1.1 Benign Tumors
25.1.2 Malignant Lesions
25.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
25.3 Surgical Approach
25.3.1 Surgical Planning
25.3.2 Orbital Surgical Planes
25.3.3 Exenteration
25.4 Postoperative Treatment
25.4.1 Local Treatment
25.4.2 Systemic Management
25.4.3 Complications and Management
25.5 Highlights
26 Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Children for Benign Lesions
26.1 Introduction
26.2 Limitations and Special Considerations
26.3 Preoperative Evaluation
26.4 Congenital Midline Lesions
26.4.1 Nasal Dermoid Cyst
26.4.2 Glioma
26.5 Middle Skull Base Lesions
26.5.1 Pituitary Adenoma
26.5.2 Craniopharyngioma
26.5.3 Rathke’s Cleft Cyst
26.6 Other Sinonasal and Skull Base Lesions
26.6.1 Schwannoma
26.6.2 Neurofibroma
26.6.3 Hemangioma
26.6.4 Papilloma
26.6.5 Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
26.7 Surgical Technique
26.8 Surgical Approaches
26.8.1 Transnasal Approach
26.8.2 Sagittal Plane
26.8.3 Coronal Plane
26.9 Highlights
27 Endoscopic Treatment of Juvenile Angiofibroma: Surgical Technique
27.1 Introduction
27.2 Diagnosis and Preoperative Management
27.3 Indications and Contraindications for Endoscopic Endonasal Approach
27.4 Surgical Settings
27.5 Surgical Instrumentation
27.6 Surgical Technique
27.6.1 Bleeding Control
27.7 Highlights
28 Juvenile Angiofibroma with Intracranial Extension
28.1 Introduction
28.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
28.3 Surgical Technique
28.3.1 Staging of Surgery
28.3.2 Outcomes
28.4 Postoperative Treatment
28.5 Highlights
29 Expanded Endonasal Approaches for Treatment of Malignancy in Children
29.1 Introduction
29.1.1 Chordoma
29.1.2 Chondrosarcoma
29.1.3 Sarcomas
29.1.4 Ewing Sarcoma
29.1.5 Olfactory Neuroblastoma
29.1.6 Germinoma
29.1.7 Lymphoma
29.2 Preoperative Evaluation
29.3 Perioperative Management
29.4 Surgical Technique
29.4.1 Anterior Cranial Fossa: Transfrontal/Transcribriform/Transplanum Approach
29.4.2 Posterior Cranial Fossa: Transclival Approach
29.5 Postoperative Management
29.6 Outcomes
29.7 Complications
29.8 Highlights
30 Open Approaches to the Anterior Skull Base in Children
30.1 Introduction
30.2 Bilateral/Unilateral Subfrontal Approach
30.2.1 Surgical Technique
30.3 The Subcranial Approach
30.3.1 Surgical Technique
30.4 Subcranial–Transfacial Approach
30.5 Midfacial Degloving Approach
30.5.1 Surgical Technique
30.6 The Combined Subcranial–Midfacial Degloving Approach
30.7 The Subcranial–Transorbital Approach
30.8 Subcranial–Le Fort I Approach
30.8.1 Reconstruction
30.9 Highlights
31 Surgical Approach to the Lateral Skull Base
31.1 Introduction
31.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
31.3 Surgical Technique
31.3.1 Preparation
31.3.2 Incision
31.3.3 External Auditory Canal Obliteration
31.3.4 Internal Carotid Artery and Internal Jugular Vein Exposure
31.3.5 Temporalis Muscle Elevation
31.3.6 Zygomatic Ostectomy
31.3.7 Mandibular Condylectomy
31.3.8 Exposure of the Subtemporal Trapezoid Muscle
31.3.9 Otologic Exposure
31.3.10 Craniotomy
31.3.11 Carotid Dissection and Eustachian Tube Resection
31.3.12 Cavernous Sinus Resection
31.3.13 Dura and Brain Resection
31.3.14 Reconstruction
31.4 Postoperative Treatment
31.5 Highlights
32 Lateral Skull Base Surgery in a Pediatric Population
32.1 Introduction
32.1.1 Anatomical Considerations in Pediatric Population
32.1.2 Demography
32.1.3 Clinical Features
32.1.4 Pathology
32.1.5 Preoperative Workup
32.1.6 Surgical Considerations
32.1.7 Surgical Procedures
32.1.8 Functional Preservation
32.1.9 Complications
32.2 Conclusion
32.3 Highlights
33 Surgery of Skull Base Meningoencephalocele
33.1 Definition and Historical Notes
33.2 Classification and Distribution
33.3 Etiology and Embryological Considerations
33.4 Clinical Presentation
33.5 Diagnosis
33.6 Treatment
33.7 Step-by-Step Endoscopic Transnasal Approach
33.8 Endoscopic Transnasal Surgical Corridors
33.9 Technical Consideration in Pediatric Endoscopic Transnasal Surgery
33.9.1 Timing of Repair
33.9.2 Anatomical Aspects
33.9.3 Intraoperative Image Guidance
33.9.4 Nasoseptal Flap
33.10 Complications and Long-term Outcomes
33.11 Highlights
34 Brain Stem Implantation
34.1 Introduction
34.1.1 History
34.1.2 Anatomy
34.1.3 Auditory Brain Stem Implant Device
34.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
34.3 Surgical Technique
34.4 Postoperative Treatment
34.4.1 Implant Activation
34.4.2 Surgical Complications
34.4.3 Outcomes
34.5 Conclusion
34.6 Highlights
35 Excision of Fibro-osseous Lesions of the Craniofacial Skeleton
35.1 Introduction
35.2 Patient Evaluation
35.3 Fibrous Dysplasia
35.4 Imaging
35.5 Management of Fibrous Dysplasia
35.5.1 Facial Bones
35.5.2 Paranasal Sinuses
35.5.3 Optic Canal
35.5.4 Temporal Bone
35.6 Ossifying Fibroma
35.7 Imaging
35.8 Management of Ossifying Fibroma
35.9 Osteoma
35.10 Imaging
35.11 Management of Osteoma
35.12 Acknowledgment
35.13 Highlights
36 Repair of Pyriform Aperture Stenosis
36.1 Introduction
36.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
36.3 Surgical Techniques
36.3.1 Transnasal Approach
36.3.2 Sublabial Approach
36.3.3 Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) (Collares et al)
36.4 Postoperative Treatment
36.5 Highlights
37 Rhinoplasty: Secondary Cleft Nasal Deformity
37.1 Introduction
37.2 Anatomy of the Nose
37.3 Preoperative Assessment
37.4 Timing of Surgery
37.5 Surgical Approach
37.6 Surgical Technique
37.7 Complications
37.8 Highlights
38 Bilateral Choanal Atresia Repair
38.1 Introduction
38.2 Surgical Technique
38.3 Discussion
38.4 Highlights
39 Cleft Lip and Palate
39.1 Introduction
39.2 Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair
39.2.1 Introduction
39.2.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
39.2.3 Surgical Technique
39.2.4 Postoperative Care
39.3 Bilateral Cleft Lip Repair
39.3.1 Introduction
39.3.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
39.3.3 Surgical Technique
39.3.4 Postoperative Care
39.4 Highlights of Cleft Lip Repair
39.5 Cleft Palate Repair
39.5.1 Introduction
39.5.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
39.5.3 Surgical Technique
39.5.4 Postoperative Care
39.6 Highlights of Cleft Palate Repair
40 Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis
40.1 Micrognathia and Pierre Robin Sequence
40.2 Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis
40.3 Preoperative Evaluation and Management
40.4 Surgical Technique
40.5 Postoperative Care and Distraction Monitoring
40.6 Complications
40.7 Conclusion
40.8 Highlights
Section IV Airway, Voice, and Swallowing
41 Surgery for Velopharyngeal Insufficiency
41.1 Introduction
41.2 Patterns of Velopharyngeal Closure
41.3 Velopharyngeal Assessment
41.4 Surgical Treatment Options
41.5 Surgical Procedures
41.5.1 Superiorly Based Pharyngeal Flap
41.5.2 Sphincter Pharyngoplasty
41.5.3 Posterior Pharyngeal Wall Augmentation
41.5.4 Furlow Palatoplasty
41.6 Highlights
42 Pediatric Tracheostomy
42.1 Introduction
42.2 Indications
42.3 Surgical Technique
42.3.1 Anatomy
42.3.2 Traditional Tracheostomy
42.3.3 Bjork Flap
42.3.4 Starplasty Tracheostomy
42.4 Intraoperative Complications
42.5 Postoperative Complications
42.6 Early Complications
42.6.1 Tube Obstruction
42.6.2 Air Leak
42.6.3 Hemorrhage
42.6.4 Accidental Decannulation
42.6.5 Infection
42.7 Late Complications
42.7.1 Granulomata
42.7.2 Airway Stenosis or Collapse
42.7.3 Peristomal and Tracheal Erosion
42.8 Mortality Rate
42.9 Home Care
42.10 Surveillance
42.11 Decannulation
42.12 Tracheocutaneous Fistula
42.12.1 Technique—Repair of Tracheocutaneous Fistula
42.13 Highlights
43 Tracheocutaneous Fistula Repair
43.1 Introduction
43.2 Preoperative Evaluation for TCF repair
43.3 Tracheocutaneous Fistula Repair
43.3.1 Secondary Closure—Description of Procedure
43.3.2 Primary Closure
43.4 Complications of Tracheocutaneous Fistula Repair
43.5 Highlights
44 Pediatric Bronchoscopy
44.1 Introduction
44.2 Instruments
44.2.1 Laryngoscopes
44.2.2 Bronchoscopes
44.2.3 Ancillary Tools
44.2.4 Imaging System
44.3 Technique
44.3.1 Types of Anesthesia
44.4 Surgical Technique
44.5 Indications
44.6 Limitations
44.6.1 Disadvantages
44.6.2 Complications
44.7 Flexible Endoscopy
44.7.1 Introduction
44.7.2 Instrument
44.7.3 Indications
44.7.4 Technique
44.7.5 Complications
44.8 Highlights
45 Surgery of Laryngomalacia
45.1 Introduction
45.2 Pathophysiology
45.3 Presentation
45.4 Symptoms
45.5 Indications for Surgery
45.6 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
45.7 Supraglottoplasty
45.8 Airway Safety
45.9 Stages of Surgery
45.10 Type of Supraglottoplasty
45.10.1 Type 1
45.10.2 Type 2
45.10.3 Type 3
45.11 Postoperative Treatment
45.12 Complications
45.13 Surgical Results
45.14 Highlights
46 Unilateral and Bilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis
46.1 Part 1 Unilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis
46.1.1 Introduction
46.1.2 Preoperative Evaluation
46.1.3 Surgical Options
46.1.4 Injection Medialization Laryngoplasty
46.1.5 Highlights
46.1.6 Unilateral Ansa Cervicalis to Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Reinnervation
46.1.7 Highlights
46.2 Part 2 Bilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis
46.2.1 Bilateral Selective Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Reinnervation
46.2.2 Highlights
47 Endoscopic Airway Surgery
47.1 Introduction
47.1.1 History and Evolution
47.1.2 Relationship of Endoscopic to Open Airway Surgery
47.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
47.2.1 History and Examination
47.2.2 Investigations
47.2.3 Anesthesia
47.3 Surgical Techniques
47.3.1 Preparation and Positioning
47.3.2 Endoscopic Airway Evaluation
47.3.3 Endoscopic Airway Surgery
47.4 Postoperative Treatment
47.5 Highlights
48 Surgical Approach to Juvenile Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
48.1 Introduction
48.1.1 General
48.1.2 Pathophysiology
48.1.3 Epidemiology
48.1.4 Presentation
48.1.5 Clinical Assessment
48.1.6 Patient Discussion
48.2 OR Preparation
48.3 OR Setup
48.3.1 Tools for Removal of Papilloma
48.4 Intraoperative Approach
48.4.1 General Treatment Principles
48.4.2 General Technique “Pearls”
48.4.3 Adjuvant Therapy
48.4.4 Note on Adjuvant Treatment
48.4.5 Technique of Intralesional Injection
48.4.6 Cidofovir
48.4.7 Safety Concerns
48.4.8 The Future of JORRP Management
48.5 Highlights
49 Laryngotracheal Reconstruction
49.1 Introduction
49.2 Definition and Classification
49.3 Evaluation, Preoperative, and Anesthesia Considerations
49.3.1 Timing of Reconstruction
49.4 Surgical Management
49.4.1 Role for Endoscopic Treatment
49.5 Open Surgical Techniques
49.5.1 Anterior Cricoid Split
49.5.2 LTR with Cartilage Grafting
49.5.3 Anterior Grafts
49.5.4 Posterior Grafts
49.5.5 Use of Stents
49.5.6 Cricotracheal Resection
49.5.7 Decannulation
49.5.8 Postoperative Considerations
49.6 Highlights
50 Partial Cricotracheal Resection
50.1 Indications
50.2 Relative Contraindications
50.3 Comparison to LTR Best Handles
50.4 Grades of Stenosis III, IV
50.4.1 Diagnostic Evaluation
50.4.2 General Surgical Approach
50.4.3 Major Pearls of the Surgery
50.5 Single Stage verses Double Stage
50.6 Extended CTR
50.7 Combined LTR and CTR
50.8 Postoperative Care
50.9 Results
50.10 Complications
50.11 Conclusion
50.12 Highlights
51 Harvesting Costal Cartilage for Laryngotracheal Reconstruction
51.1 Introduction
51.2 Indications and Contraindications
51.3 Surgical Technique
51.4 Donor Site Postoperative Care
51.5 Donor Site Complications
51.6 Highlights
52 Laryngotracheal Cleft Repair
52.1 Introduction
52.2 Embryology of Laryngotracheal Clefts
52.3 Presentation
52.4 Preoperative Evaluation and Management
52.4.1 Investigations
52.4.2 Preoperative Medical Management
52.4.3 Anesthetic Considerations
52.5 Surgical Technique
52.5.1 Endoscopic Repair
52.5.2 Open Repair
52.6 Postoperative Treatment
52.7 Highlights
53 Slide Tracheoplasty
53.1 Introduction
53.2 Preoperative Evaluation and Anesthesia
53.3 Surgical Techniques
53.3.1 Intrathoracic Slide Tracheoplasty
53.3.2 Cervical Slide Tracheoplasty
53.3.3 Slide Tracheoplasty for Tracheoesophageal Fistula
53.4 Postoperative Treatment
53.5 Highlights
Section V Pediatric Trauma
54 Facial Trauma in Pediatric Patient
54.1 Introduction
54.2 Growth and Development
54.3 Epidemiology
54.4 Preoperative Evaluation
54.5 Fractures Sites and Surgical Treatment (by Fracture Site)
54.5.1 Frontal Bone, Frontal Sinus, and Superior Orbital Fractures
54.5.2 Naso-Orbito-Ethmoid Fractures
54.5.3 Orbital Floor and Blowout Fractures
54.5.4 Nasal Fractures
54.5.5 Midface and Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures
54.5.6 Mandibular Fractures
54.5.7 Resorbable Plates
55 The Management of Temporal Bone Fractures
55.1 Introduction
55.1.1 Epidemiology
55.1.2 Pathophysiology
55.1.3 Classification
55.2 Diagnostic Approach
55.2.1 Initial Evaluation
55.2.2 Temporal Bone Fracture
55.2.3 Management
55.3 CSF Leak
55.4 Facial Nerve
55.4.1 Choice of Management
55.4.2 Surgical Technique
55.5 Hearing Loss
55.6 External Ear Injury
55.7 Other Complications
55.8 Highlights
Section VI Reconstruction
56 Regional and Local Flaps in Children
56.1 Introduction
56.2 Local and Regional Flaps
56.3 Cervicofacial Flap
56.4 Scalp Rotation Flap
56.5 Geometric Flaps
56.5.1 Bilobe Flap
56.5.2 Rhombic Flap
56.6 Interpolated Flaps for Cutaneous Defects
56.6.1 Paramedian Forehead Flap
56.7 Oral and Perioral Flaps
56.7.1 Tongue Flap
56.7.2 Facial Artery Myomucosal Flap
56.7.3 Abbé–Sabattini Cross-Lip Flap
56.7.4 Pharyngeal Flap
56.8 Temporoparietal Fascia Flap
56.9 Pericranial Flap
56.10 Submental Island Flap
56.11 Pectoralis Major Muscle or Myocutaneous Flap
56.12 Conclusion
56.13 Highlights
57 Facial Paralysis in the Pediatric Patient
57.1 Introduction
57.2 Etiology and Epidemiology
57.2.1 Congenital Facial Nerve Palsy
57.2.2 Möbius Syndrome
57.2.3 Acquired Facial Nerve Palsy
57.3 Prognosis
57.4 Treatment
57.5 Surgery
57.6 Primary Repair
57.6.1 Indications
57.6.2 Technique
57.7 Nerve Grafting: Ipsilateral and Cross-Facial
57.7.1 Indications
57.7.2 Technique
57.8 Innervated Free Flaps
57.8.1 Indications
57.8.2 Technique
57.8.3 Second-Stage Free Gracilis Transfer
57.8.4 One-Stage Free Gracilis to Masseter Facial Reanimation
57.9 Conclusion
57.10 Highlights
58 Free Flap Transfers in Head-and-Neck Reconstructions of Pediatric Patients
58.1 Introduction
58.2 Soft Tissue Free Flaps
58.2.1 Anterolateral Thigh Flap
58.2.2 Radial Forearm Free Flap
58.2.3 Rectus Abdominis Flap
58.2.4 Latissimus Dorsi Free Flap
58.2.5 Parascapular Fasciocutaneous Free Flap
58.2.6 Osteocutaneous Free Flaps
58.3 Highlights
59 Otoplasty
59.1 Introduction
59.2 Anatomy of the Ear
59.3 Preoperative Assessment
59.4 Timing of Surgery
59.5 Nonsurgical Treatment
59.5.1 Ear Molding
59.6 Otoplasty Surgical Technique
59.7 Complications
59.8 Highlights
Index
Additional MedOne Access Information
| An aparitie | 9 Dec. 2020 |
| Autor | Dan M. Fliss, Ari DeRowe |
| Dimensiuni | 26.92 x 19.56 cm |
| Editura | Thieme |
| Format | Hardcover |
| ISBN | 9783132414273 |
| Limba | Engleza |
| Nr pag | 617 |






Clientii ebookshop.ro nu au adaugat inca opinii pentru acest produs. Fii primul care adauga o parere, folosind formularul de mai jos.