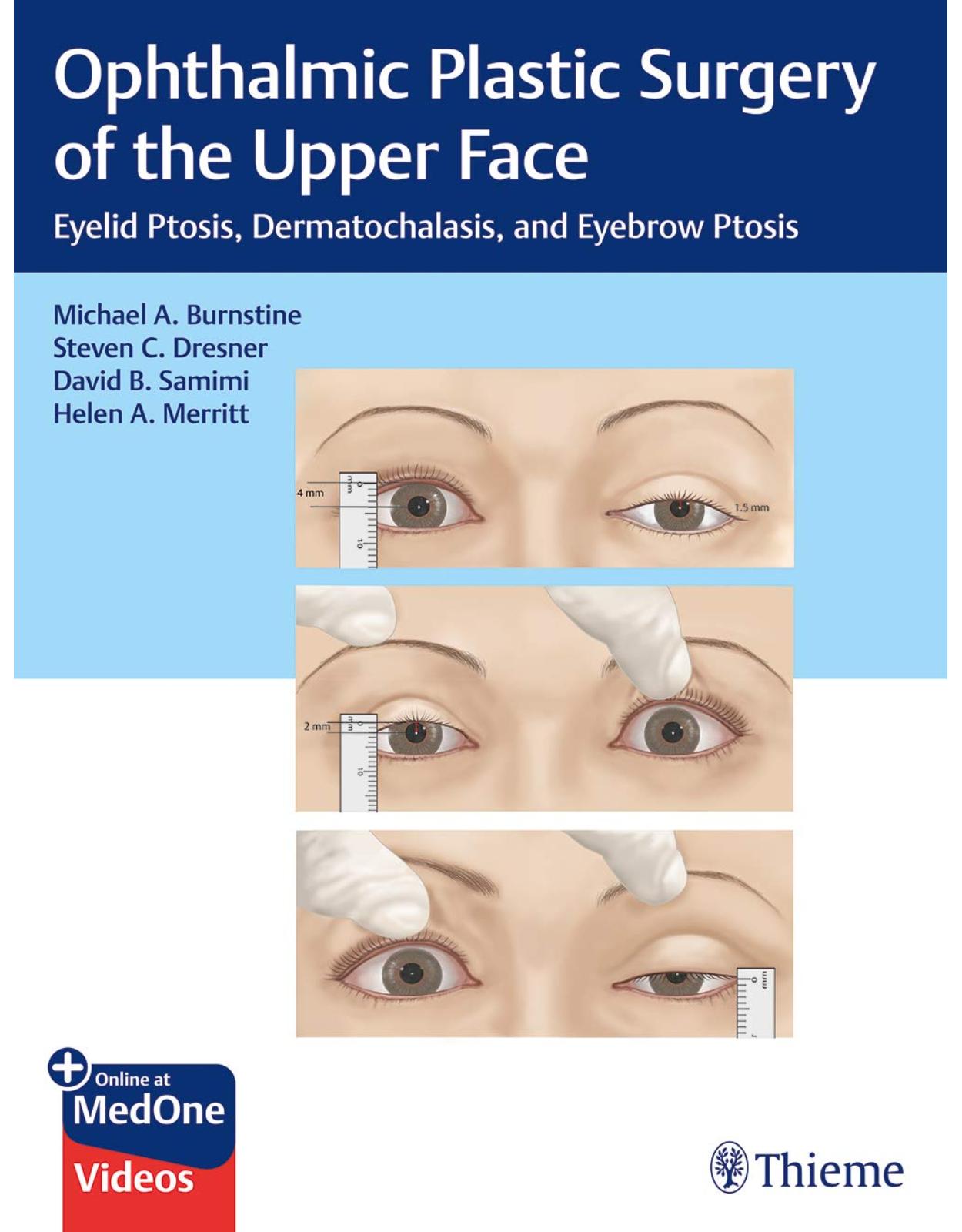
Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery of the Upper Face
Livrare gratis la comenzi peste 500 RON. Pentru celelalte comenzi livrarea este 20 RON.
Disponibilitate: La comanda in aproximativ 4-6 saptamani
Editura: Thieme
Limba: Engleza
Nr. pagini: 288
Coperta: Hardcover
Dimensiuni: 221 x 284 x 20 mm
An aparitie: 15 Nov. 2019
Description:
The definitive resource on cutting-edge oculoplastic surgery of the upper face, eyelids, and eyebrows
While an estimated 1.5 million brow and upper eyelid surgery procedures are performed worldwide each year, this book is the first published ophthalmologic text with detailed coverage focused solely on this topic. Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery of the Upper Face: Eyelid Ptosis, Dermatochalasis, and Eyebrow Ptosis by distinguished oculofacial plastic surgeons and educators Michael A. Burnstine, Steven C. Dresner, David B. Samimi, Helen A. Merritt, and an impressive group of international experts fills a void in the literature. The succinct, richly illustrated text covers classification, anatomy, evaluation, and a wide spectrum of surgical approaches for each condition. Surgical videos are included.
Organized by 7 sections and 39 chapters, the book begins with clinical assessment of patients who present with upper eyelid and eyebrow conditions, followed by evidenced-based treatment protocols. All procedural chapters follow a consistent format, enabling readers to classify problems, review surgical steps, and consider key issues associated with each condition and corrective procedure. Mechanical, involutional, neurogenic, myogenic, and syndromic blepharoptoses detailed in Sections 2 to 6 include etiology, diagnosis, management, and diverse state-of-the-art resection, repair, lift, fill, and augmentation techniques.
Key Features
Each procedural chapter includes an introduction, risks, benefits, informed consent, indications, relative contraindications, a preoperative checklist, required instrumentation, a step-by-step approach for surgeons beginning their career, and refined tips for more experienced surgeons.
High quality full-color operative photographs enhance knowledge of the most salient operative steps, while before and after photos demonstrate the evidence-based efficacy of each surgery.
Chapters focused on brow surgery detail a full range of surgical and nonsurgical approaches—from contouring options and direct elevation to fillers and neuromodulators.
This is a must-have surgical resource for ophthalmology, otolaryngology, and plastic surgery residents and practitioners. The highly practical, reader-friendly text facilitates greater understanding of the clinical implications of each ophthalmic surgery approach, thereby helping surgeons achieve improved cosmetic results.
Table of Contents:
Section I Introduction
1 Ptosis Classification
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Ptosis Classification
1.3 Preoperative Assessment
1.3.1 History of Present Illness
1.3.2 Physical Examination
1.4 Upper Eyelid Ptosis Classification
1.4.1 Aponeurotic Ptosis
1.4.2 Myogenic Ptosis
1.4.3 Mechanical Ptosis
1.4.4 Neurogenic Ptosis
1.4.5 Pseudoptosis
1.5 Eyebrow Ptosis Classification
1.6 Clinical Decision-Making
1.7 Photographing the Patient
1.8 Informed Consent
1.9 Principles of Surgical Correction
1.10 When Not to Operate
1.11 Postoperative Complications
1.12 Aesthetic Concerns for Upper Eyelid and Eyebrow Rejuvenation
References
2 Aesthetic Anatomy of the Upper Face
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Skin
2.3 Subcutaneous Tissue and Fat Compartments
2.4 Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System
2.5 Retaining Ligaments, Canthal Tendons, and Orbital Septum
2.6 Mimetic Muscles and Eyelid Retractors
2.7 Deep Fat Compartments
2.8 Nervous Innervation to the Upper Eyelid and Forehead
2.8.1 Sensory
2.8.2 Motor
2.9 Blood Supply
2.9.1 Forehead
2.9.2 Eyelid
2.10 Lymphatic Drainage
2.10.1 Forehead
2.10.2 Eyelid
2.11 Unique Considerations for the Upper Facial Surgeon: Facial Danger Zones
2.12 Unique Anatomical Considerations for the Eyelid Surgeon
2.12.1 Anterior Lamella
2.12.2 Middle Lamella
2.12.3 Posterior Lamella
2.12.4 Eye Protective Mechanisms
References
3 Anatomic Considerations in the Aesthetic Surgery of the Upper Face
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Racial Differences
3.2.1 Eyelid Skin
3.2.2 Upper Eyelid Crease
3.2.3 Epicanthal Fold
3.2.4 Tarsal Plate
3.2.5 Eyebrow Height and Contour
3.3 Gender Differences
3.3.1 Eyelid Skin
3.3.2 Eyelid Dimensions
3.3.3 Eyebrow Height and Contour
3.4 Conclusions
References
Section II Mechanical Ptosis
4 Mechanical Ptosis: Etiology and Management
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Benign Eyelid Lesions
4.3 Malignant Eyelid Lesions
4.4 Orbital Lesions
4.5 Periorbital Infections and Inflammation
4.6 Other Considerations
4.7 Summary
References
5 Upper Blepharoplasty
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Goals of Treatment
5.3 Risks
5.4 Benefits
5.5 Informed Consent
5.6 Indications
5.7 Contraindications
5.8 The Procedure
5.8.1 Preoperative Checklist
5.8.2 Instruments Needed
5.8.3 Sutures Used
5.8.4 Operative Technique: Step by Step
5.8.5 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
5.8.6 Postoperative Care Checklist
5.9 Complications and Their Management
References
6 Double Eyelid Surgery
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Anatomical Considerations
6.2.1 The Eyelid Crease and Fold
6.2.2 The Medical Canthal Area
6.2.3 The Lateral Canthal Area
6.3 Goals of Intervention/Indications
6.4 Risks of the Procedure
6.5 Benefits of the Procedure
6.6 Informed Consent
6.7 Contraindications
6.8 The Procedure
6.8.1 Instruments Needed
6.8.2 Preoperative Checklist
6.8.3 The Operative Technique
6.8.4 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
6.8.5 Postoperative Care Checklist
6.9 Complications and Their Management
6.10 Alternative Approaches to Double Eyelid Surgery
References
7 A Guide to Eyebrow Contouring Options
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Evolving Trends in Brow Beauty
7.2.1 History of Eyebrow Aesthetics
7.2.2 Volume and Facial Aging
7.2.3 Eyebrow Height and Proportions
7.3 Patient Assessment
7.3.1 History
7.3.2 Physical Exam Checklist
7.4 Risks of Surgery
7.5 Choosing the Best Procedure/Physician Decision-Making
7.6 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
7.6.1 Upper Eyelid Considerations
7.6.2 The Role of Nonsurgical Adjuncts
7.6.3 Managing Asymmetry
7.6.4 Minimizing Hair Loss
8 Direct Eyebrow Elevation
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Relevant Anatomy
8.3 Goals of Intervention, Indications, and Benefits of the Procedure
8.4 Risks of the Procedure
8.5 Preoperative Considerations and Patient Selection
8.6 Informed Consent
8.7 Relative Contraindications
8.8 Procedure
8.8.1 Instrumentation
8.8.2 Preoperative Checklist
8.8.3 Operative Technique
8.8.4 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
8.8.5 Postoperative Care
8.9 Complications and Their Management
References
9 Internal Eyebrow Lift
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Anatomic Considerations of the Upper Facial Continuum
9.3 Goals of Intervention
9.4 Risks
9.5 Benefits
9.6 Informed Consent
9.7 Indications
9.8 Contraindications
9.9 Patient Assessment
9.9.1 Medical History
9.9.2 Ophthalmic History
9.9.3 Ophthalmic Examination
9.9.4 Anatomic Evaluation: The Eyelid and Eyebrow Subunits
9.10 Preoperative Checklist
9.11 The Procedure
9.11.1 Instrumentation Needed
9.11.2 Sutures
9.11.3 Operative Technique
9.12 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
9.13 Postoperative Care Checklist
9.14 Complications and Their management
9.14.1 Bleeding
9.14.2 Infection
9.14.3 Nerve Damage
9.14.4 Postoperative Lagophthalmos and Dry Eye
9.14.5 Residual Aesthetic Deformity
9.14.6 Skin Dimpling
9.15 Summary
References
10 Midforehead Browlift Technique
10.1 Introduction
10.2 Goals of Intervention/Indications
10.3 Risks of the Procedure
10.4 Benefits of the Procedure
10.5 Informed Consent
10.6 Contraindications
10.7 Preoperative Assessment
10.8 The Procedure
10.8.1 Instruments Needed
10.8.2 Operative Technique
10.9 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
10.10 Postoperative Care Checklist
10.11 Complications and Their Management
10.12 Conclusion
References
11 Open Coronal Pretrichial Browlift Surgery
11.1 Introduction
11.2 Unique Anatomical Considerations in Coronal Brow Lifting
11.2.1 The Eyebrow
11.2.2 The Anatomic Layers
11.2.3 The Muscles of Elevation and Depression
11.2.4 The Sensory Supply
11.2.5 The Facial Nerve
11.2.6 The Vascular Supply
11.3 Patient Evaluation
11.3.1 Forehead Length and Contour
11.3.2 Eyebrow Shape and Contour
11.3.3 Forehead Rhytids
11.3.4 Nasal Root
11.4 Goals of Intervention/Indications
11.5 Risks of the Procedure
11.6 Benefits of the Procedure
11.7 Contraindications
11.8 Informed Consent
11.9 The Procedure
11.9.1 Instruments Needed
11.9.2 Sutures Used
11.9.3 Preoperative Checklist
11.9.4 The Operative Technique
11.10 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
11.11 Postoperative Care Checklist
11.12 Complications and Their Management
11.12.1 Expanding Hematoma
11.12.2 Scarring
11.12.3 Postoperative Brow Asymmetry
11.12.4 Facial Nerve Damage
11.12.5 Scalp and Forehead Numbness
11.12.6 Alopecia
11.13 Alternative Approaches to the Open Browlift
References
Bibliography
12 Pretrichial Temporal Browlift
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Goals of Intervention/Indications
12.3 Risks of Procedure
12.4 Benefits of Procedure
12.5 Contraindications
12.6 Informed Consent
12.7 Preoperative Evaluation
12.8 The Procedure
12.8.1 Instrumentation
12.8.2 Preoperative Checklist
12.8.3 Surgical Technique
12.9 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
12.10 Postoperative Care Checklist
12.11 Complications
12.11.1 Scarring
12.11.2 Suture Granuloma
12.11.3 Undercorrection
12.11.4 Overcorrection
12.12 Conclusion
References
13 Minimally Invasive Su-Por–Suture Temporal Brow Suspension: The Lift and Fill Technique
13.1 Introduction
13.2 Goals of Intervention/Indications
13.2.1 Risks of the Procedure
13.2.2 Benefits of the Procedure
13.2.3 Informed Consent
13.3 Contraindications
13.4 The Procedure
13.4.1 Instruments Needed
13.4.2 Preoperative Checklist
13.4.3 Operative Technique
13.5 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
13.6 Postoperative Care Checklist
13.7 Complications and Their Management
References
14 Endoscopic Upper Face and Eyebrow Lifting
14.1 Introduction
14.2 Goals of Intervention
14.3 Risks
14.4 Informed Consent
14.5 Indications
14.6 Contraindications
14.7 The Procedure
14.7.1 Preoperative Checklist
14.7.2 Instruments Needed
14.7.3 Closure
14.7.4 Local Anesthetic
14.7.5 Fat Grafting
14.7.6 Incision Placement
14.7.7 Operative Technique
14.8 Postoperative Care Checklist
14.9 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
14.10 Complications and Their Management
14.11 Conclusions
References
15 Nonsurgical Management Techniques: Fillers and Neuromodulators
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Properties of Botulinum Toxins and Periocular Fillers
15.2.1 Botulinum Toxin Properties
15.2.2 Periocular Fillers Properties
15.3 Single Therapy and Combination Treatments in the Upper Face
15.3.1 Glabellar Frown Lines
15.3.2 Crow’s-Feet
15.3.3 Horizontal Forehead Lines
15.3.4 Brow Lifting and Shaping
15.3.5 Hypertrophic Orbicularis Oculi
15.3.6 Midface
15.3.7 Temple
15.4 Conclusion
References
16 Fat Augmentation of the Brow
16.1 Introduction
16.2 Goals of Intervention
16.3 Risks of Fat Grafting
16.4 Benefits of Fat Grafting
16.5 Informed Consent
16.6 Indications
16.7 Contraindications
16.8 Preoperative Checklist
16.8.1 Instrumentation
16.8.2 Operative Technique: Step by Step
16.9 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
16.10 Postoperative Care Checklist
16.11 Complications and Their Management
16.12 Conclusion
References
Section III Involutional Ptosis
17 Involutional Ptosis: Etiology and Management
17.1 Introduction
17.2 Etiology
17.3 Clinical Presentation
17.4 Evaluation
17.4.1 Evaluation of Eyelid
17.5 Management
References
18 External Levator Advancement with Orbicularis-Sparing Technique
18.1 Introduction/Goals of Intervention
18.2 Risks
18.3 Benefits
18.4 Informed Consent
18.5 Indications
18.6 Relative Contraindications
18.7 The Procedure
18.7.1 Preoperative Checklist
18.7.2 Instruments Needed
18.7.3 Sutures Used
18.7.4 The Operative Technique: Step by Step
18.8 Postoperative Care Checklist
18.9 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
18.10 Complications and Their Management
18.10.1 Undercorrection
18.10.2 Overcorrection
18.10.3 Lagophthalmos
18.10.4 Unsatisfactory Eyelid Contour or Eyelid Crease Asymmetry
18.10.5 Wound Infection
18.10.6 Retrobulbar Hemorrhage
18.11 Conclusion
References
19 Small Incision Anterior Levator Advancement
19.1 Introduction
19.2 Goals/Indications
19.3 Risks of the Procedure
19.4 Benefits of the Procedure
19.5 Contraindications
19.5.1 Absolute Contraindications
19.5.2 Relative Contraindications
19.6 Informed Consent
19.7 The Procedure
19.7.1 Instruments Needed
19.7.2 Preoperative Checklist
19.7.3 Operative Technique
19.8 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
19.9 Postoperative Care Checklist
19.10 Complications and Their Management
References
20 Müller’s Muscle–Conjunctival Resection
20.1 Introduction
20.2 Special Preoperative Considerations
20.2.1 Margin Reflex Distance 1
20.2.2 Phenylephrine Test
20.2.3 Determining the Amount of Müller’s Muscle–Conjunctival Resection
20.3 Risks
20.4 Benefits
20.5 Informed Consent
20.6 Contraindications
20.7 Instrumentation
20.8 Preoperative Checklist
20.9 Operative Technique
20.10 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
20.11 Postoperative Management
20.12 Complications and Their Management
20.13 Acknowledgment
References
21 Dresner’s Modification of Müller’s Muscle–Conjunctival Resection
21.1 Introduction
21.2 Indications
21.3 Risks
21.4 Benefits
21.5 Informed Consent
21.6 Contraindications
21.7 Instrumentation
21.8 Preoperative Checklist
21.9 Operative Technique
21.10 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
21.11 Results
21.12 Complications and Their Management
21.13 Conclusion
References
22 Posterior White Line Advancement
22.1 Introduction
22.2 Relevant Anatomy
22.3 Indications
22.4 Risks
22.5 Benefits
22.6 Informed Consent
22.7 Contraindications
22.8 Instrumentation
22.9 Preoperative Checklist
22.10 Operative Technique
22.10.1 The White Line Advancement for Aponeurotic Ptosis
22.10.2 Levatorpexy for Congenital Ptosis
22.11 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
22.12 Complications and Their Management
22.13 Conclusions
References
23 The Fasanella–Servat Procedure
23.1 Introduction
23.2 Indications
23.3 Risks
23.4 Benefits
23.5 Informed Consent
23.6 Contraindications
23.7 Instruments Needed
23.8 Preoperative Checklist
23.9 Operative Technique
23.10 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
23.11 Results
23.12 Complications and Their Management
23.13 Conclusion
References
24 Combined Upper Blepharoplasty and Ptosis Repair
24.1 Introduction
24.2 Clinical Evaluation and Indications for Surgery
24.3 Combined Müller’s Muscle–Conjunctival Resection and Blepharoplasty
24.4 Combined Fasanella–Servat and Blepharoplasty
24.5 Combined Levator Aponeurotic Advancement and Blepharoplasty
24.5.1 Indications
24.5.2 Contraindications
24.5.3 Instrumentation
24.5.4 Preoperative Checklist
24.5.5 Operative Technique
24.6 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
24.7 Postoperative Management
24.8 Complications and Their Management
25 Floppy Eyelid Syndrome Repair with Concomitant Ptosis Repair
25.1 Introduction
25.2 Goals of Intervention/Indications
25.2.1 Risks of the Procedure
25.2.2 Benefits of the Procedure
25.3 Informed Consent
25.4 Contraindications
25.5 Preoperative Assessment
25.6 Operative Technique
25.6.1 Instruments Needed
25.6.2 Surgical Technique
25.7 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
25.8 Postoperative Care Checklist
25.9 Complications
References
26 Management of Lacrimal Gland Prolapse
26.1 Introduction and Anatomy
26.2 Goals of Intervention
26.3 Risks
26.4 Benefits
26.5 Contraindications
26.5.1 Surgical Procedure
26.5.2 Instruments Needed
26.5.3 Operative Technique: Step by Step
26.6 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
26.7 Postoperative Management and Complications
References
Section IV Myogenic Ptosis
27 Myogenic Ptosis: Etiology and Management
27.1 Introduction
27.2 Static Myogenic Ptosis
27.3 Progressive Myogenic Ptosis
References
28 Static Myogenic Ptosis: Evaluation and Management
28.1 Introduction
28.2 Causes and Syndromic Associations of Static Myopathic Ptosis
28.2.1 Isolated Congenital Ptosis
28.2.2 Static Myopathic Ptosis with Associated Periocular Anomalies
28.2.3 Congenital Ptosis with Aberrant Innervation
28.2.4 Trauma
28.3 History
28.3.1 Personal History of Ptosis
28.3.2 Family History of Ptosis
28.4 The Physical Examination
28.4.1 The Eyelid and Adnexal Examination
28.4.2 The Eye Examination
28.5 Management
28.5.1 Observation
28.5.2 Timing of Surgical Intervention
28.5.3 The Surgical Approach
28.6 Conclusions
References
29 Surgical Management of Levator Function Less Than 4 mm
29.1 Introduction
29.2 History of Frontalis Sling
29.2.1 Patterns of Sling
29.2.2 Sling Materials
29.2.3 Fixation of Sling to Eyelid Tarsus
29.3 Indications
29.4 Consequences
29.5 Unique Considerations in Frontalis Suspension
29.5.1 Congenital Cases
29.5.2 Acquired Cases
29.6 Risks of the Procedure
29.7 Benefits of the Procedure
29.8 Relative Contraindications
29.9 Informed Consent
29.10 The Procedure
29.10.1 Surgical Supplies and Equipment
29.10.2 Preoperative Checklist
29.10.3 Operative Technique
29.11 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
29.12 Postoperative Care Checklist
29.13 Complications and Their Management
29.13.1 Early Complications
29.13.2 Late Complications
References
30 Surgical Management of Static Congenital Ptosis with Levator Function between 4 and 10 mm
30.1 Introduction
30.2 The Anatomy of the Eyelid Crease
30.3 Preoperative Assessment
30.3.1 Indications
30.3.2 Consequences of Levator Resection
30.3.3 Risks of the Procedure
30.3.4 Benefits of the Procedure
30.3.5 Relative Contraindications
30.3.6 Alternatives
30.4 Informed Consent
30.5 Instrumentation
30.6 The Levator Resection Procedure
30.7 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
30.8 Postoperative Care
30.9 Complications and Their Management
30.10 Conclusion
References
31 Progressive Myogenic Ptosis: Evaluation and Management
31.1 Introduction
31.2 Causes of Progressive Myopathic Ptosis
31.2.1 Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy
31.2.2 Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia
31.2.3 Myotonic Dystrophies
31.2.4 The Masquerader of Progressive Myopathic Ptosis
31.3 History and Physical Examination
31.3.1 The History
31.3.2 Physical Examination
31.4 Management of Progressive Myopathic Ptosis
31.4.1 Timing of Repair
31.4.2 Our Workhorse Procedure
31.5 Conclusions
References
32 Syndromic Blepharoptoses
32.1 Introduction
32.2 Aberrant Innervation Syndromes
32.3 Static Myopathic Ptoses Involving the Extraocular Muscles
32.4 Progressive Myopathic Ptoses that Affect the Levator and Other Muscle Groups Presenting in Childhood
32.5 Progressive Myopathic Ptoses Seen in Adulthood
32.6 Management and Conclusions
References
Section V Neurogenic Ptosis
33 Neurogenic Ptosis: Diagnosis and Management
33.1 Introduction
33.2 Neuroanatomic Considerations
33.2.1 Cortical and Supranuclear Pathways
33.2.2 Oculomotor Nerve
33.2.3 Oculosympathetic Pathway
33.2.4 Neuromuscular Junction
33.3 Localization
33.3.1 Supranuclear/Cortical Localization
33.3.2 Brainstem Localization
33.3.3 Spinal Cord and Paravertebral Ganglia Localization
33.3.4 Carotid Artery and Cavernous Sinus Localization
33.3.5 Nuclear Localization
33.3.6 Infranuclear Localization
33.4 Aberrant Innervation Syndromes
33.4.1 Compressive/Trauma
33.4.2 Marin-Amat’s Syndrome
33.4.3 Synkinesis
33.5 Diseases of the Neuromuscular Junction
33.5.1 Myasthenia Gravis
33.5.2 Lambert–Eaton Syndrome
33.6 Congenital Presentations
33.6.1 Third Nerve Palsy
33.6.2 Congenital Horner’s Syndrome
33.7 Summary
References
Section VI Pseudoptosis
34 Pseudoptosis: Evaluation and Management
34.1 Introduction
34.1.1 Dermatochalasis
34.1.2 Vertical Strabismus
34.1.3 Contralateral Eyelid Retraction
34.1.4 Enophthalmos
34.1.5 Ocular Abnormalities
34.1.6 Eyelid Protractor Overaction
References
Section VII Additional Considerations in Upper Facial Surgery
35 Eyelash Ptosis Management
35.1 Introduction
35.2 Anatomical Considerations
35.2.1 Eyelash Cilia
35.2.2 Levator Aponeurosis and Eyelid Crease
35.3 Goals of Intervention/Indications
35.4 Risks of the Procedure
35.5 Benefits of the Procedure
35.6 Informed Consent
35.7 Contraindications
35.8 Procedure
35.8.1 Instruments Needed
35.8.2 Preoperative Checklist
35.8.3 Operative Technique
35.8.4 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
35.8.5 Postoperative Care Checklist
35.9 Complications and Their Management
References
36 Blepharoptosis Reoperation
36.1 Introduction
36.2 Anatomical Considerations
36.3 Goals of Intervention/Indications
36.4 Risks of the Procedure
36.5 Benefits of the Procedure
36.6 Informed Consent
36.7 Contraindications
36.8 Procedure
36.8.1 Instruments Needed
36.8.2 Preoperative Checklist
36.8.3 Operative Technique
36.8.4 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
36.8.5 Postoperative Care Checklist
36.9 Complications and Their Management
References
37 Nonsurgical Management of Ptosis
37.1 Introduction
37.2 Mechanical Eyelid Elevation
37.2.1 Eyelid Crutches
37.2.2 Eyelid Taping
37.2.3 Haptic Contact Lens
37.3 Pharmacologic Eyelid Elevation
37.3.1 Topical Therapy
37.3.2 Neurotoxin Injections
37.4 Management of Ptosis in the Anophthalmic Patient
37.5 Management of Pseudoptosis with Filler Injection
References
38 Unique Considerations in Upper Facial Surgery
38.1 Introduction
38.2 Perioperative Medications
38.2.1 Blood-Thinner Considerations
38.2.2 Classes of Blood Thinners
38.2.3 Balancing Thrombotic Risks and Bleeding Risks
38.2.4 Time to Stop Blood Thinners Preoperatively
38.2.5 Supplements and Other Considerations
38.3 Perioperative Antibiotic Considerations
38.3.1 Current Practice Patterns in Oculofacial Plastic Surgery
38.3.2 Patterns and Rates of Surgical Site Infection
38.3.3 Preoperative Recommendations
38.3.4 Perioperative Recommendations
38.3.5 Postoperative Recommendations
38.4 Energy Devices
38.4.1 Types of Devices
38.4.2 Fire Risk and the Triad
38.4.3 Effects of the Plume
38.5 Conclusions
References
39 Staying Out of Trouble: Strategies Based on Recent OMIC Oculofacial Plastic Surgery Claims
39.1 Introduction
39.2 Particular Problem Areas in the Practice of Upper Facial Plastic Surgery
39.2.1 Blepharoplasty and Ptosis Repair
39.2.2 Brow Lifting
39.2.3 Invasive Skin Treatments
39.3 Fillers and Autologous Fat
39.4 Goals for the Upper Facial Surgeon
39.4.1 Establishing the Correct Diagnosis
39.4.2 Knowing When to Say No to Treatment
39.4.3 Effective Communication
39.4.4 Surgical Plan and Execution
39.4.5 Patient Follow-Up
39.4.6 Actively Manage Complications
39.4.7 Revisit Patient Expectations Frequently
39.5 The Unhappy Patient: Cosmetic Dissatisfaction and Patient Expectations
39.5.1 Refunds
39.5.2 I’m Sorry Laws
39.6 Expert Tips/Pearls/Suggestions
39.7 Coping with the Process of a Malpractice Claim
39.8 Conclusions
References
39.9 Appendix A
39.9.1 Informed Consent for Ptosis Surgery (Droopy Eyelid Surgery)
39.10 Appendix B
39.10.1 Patient Cosmetic Surgical Agreement
Index
Medone Additional Information
| An aparitie | 15 Nov. 2019 |
| Autor | Michael Burnstine, Steven Dresner, David Samimi |
| Dimensiuni | 221 x 284 x 20 mm |
| Editura | Thieme |
| Format | Hardcover |
| ISBN | 9781626239210 |
| Limba | Engleza |
| Nr pag | 288 |
-
1,32700 lei 1,20500 lei









Clientii ebookshop.ro nu au adaugat inca opinii pentru acest produs. Fii primul care adauga o parere, folosind formularul de mai jos.